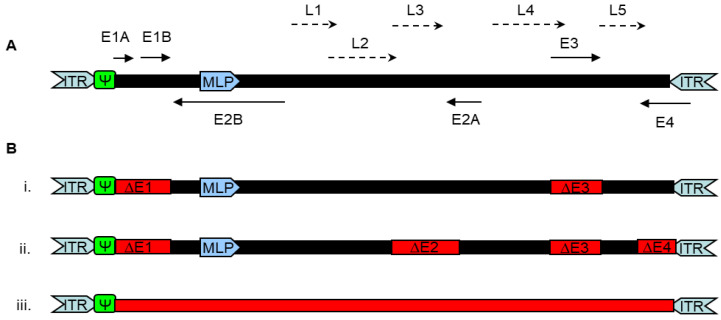
Figure 1.
Schematic overview over the wild-type adenovirus and recombinant adenoviral vector genomes. (A) Map of the wild-type adenovirus genome and its transcription units. The central, solid line represents (black) the viral genome. Positions of the left and right inverted terminal repeats (ITRs, grey), the packaging signal (Ψ, green), the early transcription units (E1A, E1B, E2A, E2B, E3, and E4 in solid arrow), and the late transcription units (major late promoter (MLP), blue; L1–L5 in dashed arrow) are shown. Arrows indicate the direction of transcription. (B) Different generations of recombinant adenoviral vectors used in gene therapy. Elements shown in red represent deletions providing space for insertion of transgene cassette. i. First-generation adenoviral vectors lacking E1 and/or E3. ii. Second-generation adenoviral vectors with multi-deletions. iii. High-capacity adenoviral vectors (HCAdV) with all viral coding regions deleted.