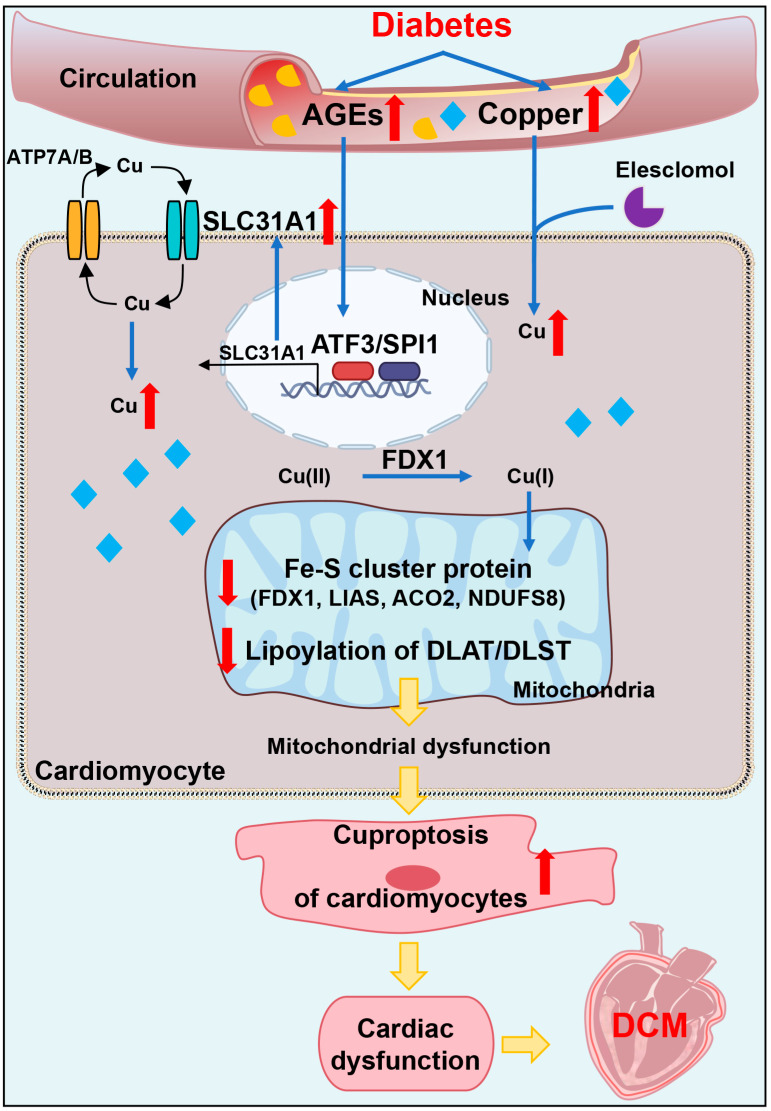
Figure 7.
Schematic of mechanisms of AGEs–CuCl2-induced cuproptosis via ATF3/SPI1/SLC31A1 pathway in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Excessive AGEs and copper in diabetes upregulated copper importer SLC31A1 through ATF3/SPI1, thereby mediating copper accumulation in cardiomyocytes, disturbing copper homeostasis and promoting cuproptosis. This promoted the decline of Fe–S cluster protein (FDX1, LIAS, NDUFS8 and ACO2) and decreased lipoylation of DLAT- and DLST-aggravated mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiomyocytes and resulted in myocardial dysfunction.