Figure 2.
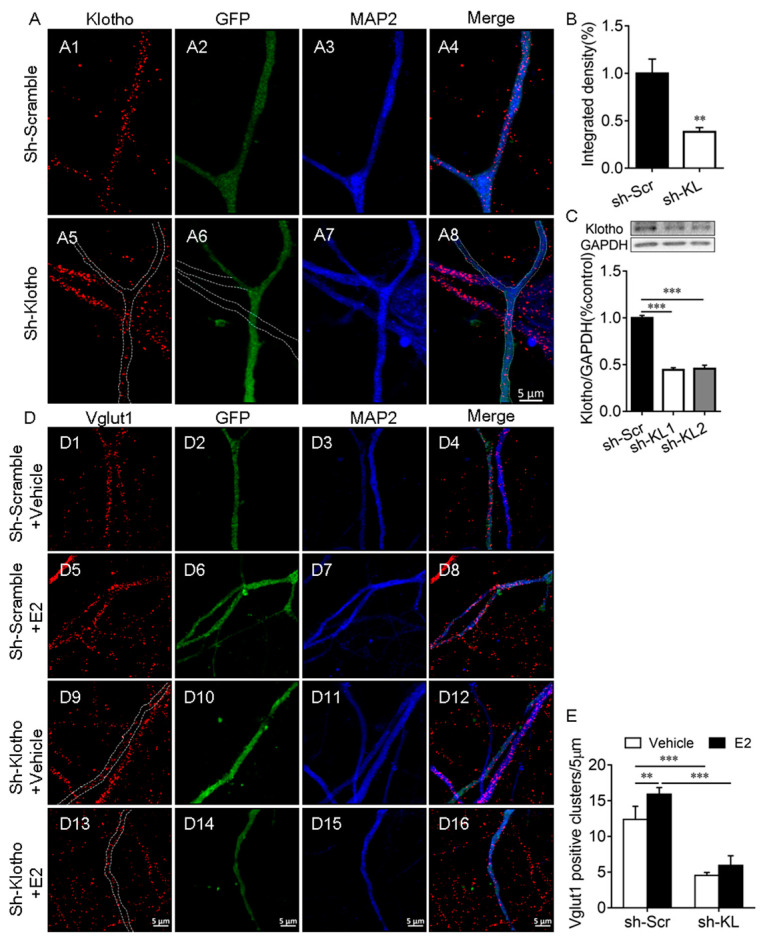
Klotho played an essential role in the E2-mediated increase in the number of Vglut1-positive clusters in hippocampal neurons. Primary cultured hippocampal neurons were transfected with a vector encoding scrambled control shRNA (sh-Scr, (A1–A4)) or Klotho shRNA (sh-KL, (A5–A8)) at Div10, and the neurons were fixed for double-immunostaining with anti-KL (red) and anti-MAP2 (blue) antibodies at Div14. The dashed lines in (A6) show the dendrites of the non-transfected neuron, which did not express Klotho shRNA-GFP (A). Quantification of KL expression in cultured hippocampal neurons (B). Two different Klotho shRNAs, sh-KL #1 and sh-KL# 2, were designed. Vectors encoding sh-Scr and sh-KL were introduced into the hippocampal neurons by electroporation at the time of plating, and the Western blot result (C) showed that the expression of shRNA #1 and #2 reduces klotho (130 kDa) expression effectively. We used sh-KL #1 in subsequent experiments. Cultured hippocampal neurons were transfected with a vector encoding sh-Scr (D1–D8) and sh-KL (D9–D16) at Div10, and the cultures at Div13 were treated with the vehicle (D1–D4, D9–D12) or 10 nM E2 (D5–D8, D13–D16) for 48 h before fixing for double-immunostaining with antibodies specific to Vglut1 (red) and MAP2 (blue; D). Quantification of Vglut1-positive clusters (E). One-way and two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.