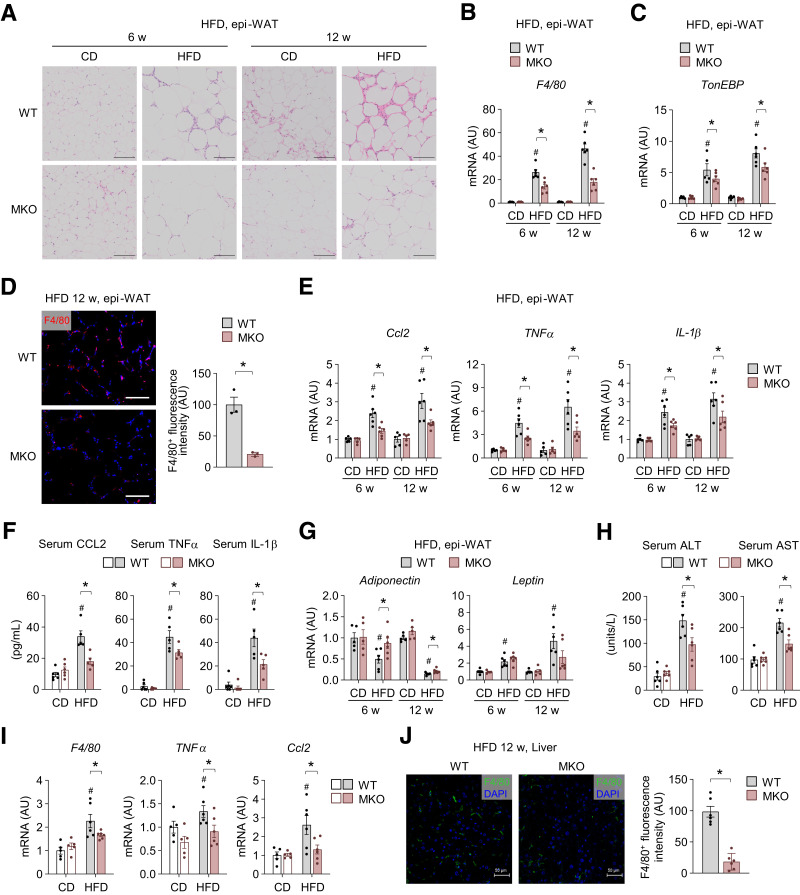
Figure 2.
Myeloid TonEBP deficiency reduces HFD-induced macrophage accumulation and inflammation in adipose tissue and the liver. A–J: WT and MKO mice were fed CD or HFD for 6 and 12 weeks. A: Representative images of H-E–stained sections of epi-WAT from mice fed CD (n = 5) or HFD (n = 6). B and C: mRNA levels of F4/80 (B) and TonEBP (C) in epi-WAT from mice fed CD (n = 5) or HFD (n = 6). D: Representative images (left) and quantification (right) of F4/80 immunostaining in epi-WAT of mice fed HFD for 12 weeks (n = 3). E: mRNA levels of Ccl2, TNF-α, and IL-1β in epi-WAT from mice fed CD (n = 5) or HFD (n = 6). F: Serum levels of CCL2, TNF-α, and IL-1β in mice fed CD (n = 6) or HFD (n = 5) for 12 weeks. G: mRNA levels of adiponectin and leptin in epi-WAT from mice fed CD (n = 5) or HFD (n = 6). H–J: WT and MKO mice were analyzed after 12 weeks on CD or HFD (n = 6). H: Serum ALT and AST concentrations. I: mRNA levels of F4/80, TNF-α, and Ccl2 in the liver. J: Representative images (left) and quantification (right) of F4/80 immunostaining in livers of HFD-fed mice (n = 6). n represents the number of biologically independent animals (or samples). All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Scale bars, 100 μm (A) and 50 μm (D and J). P values were determined with ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. #P < 0.05 vs. CD; *P < 0.05. AU, arbitrary units; w, weeks.