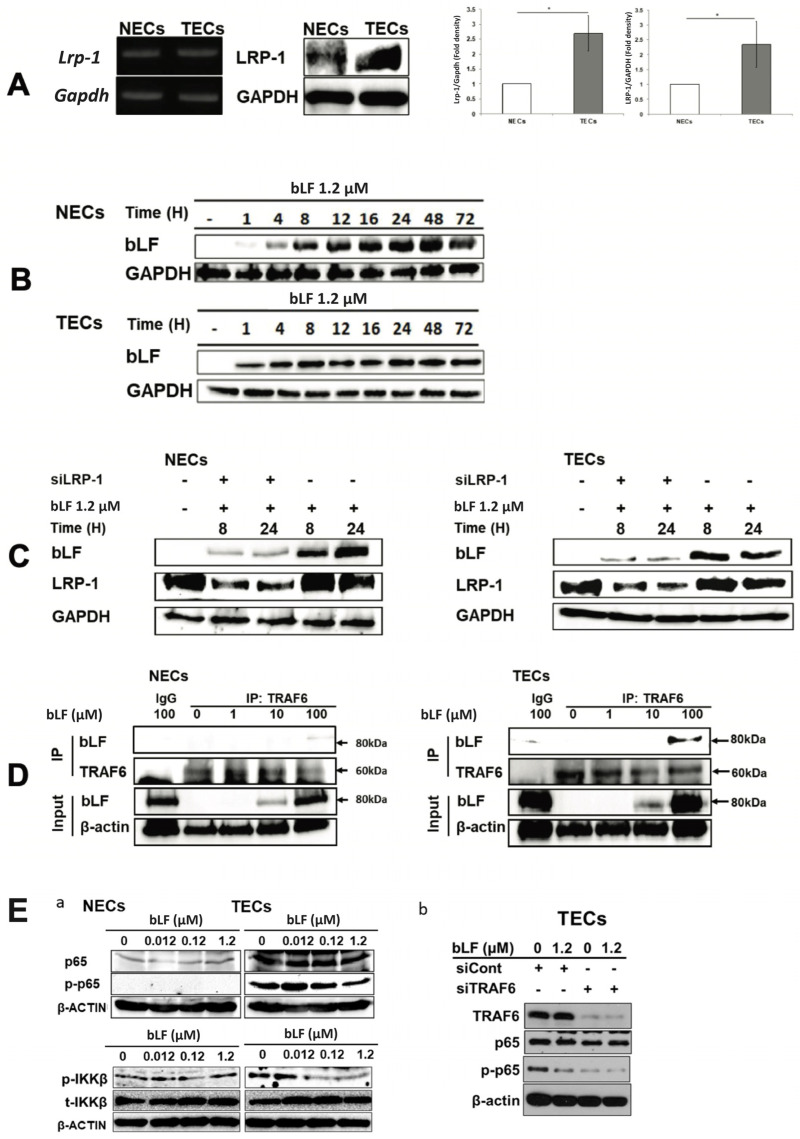
Figure 4.
bLF receptor and its role as an internalization factor for bLF in NECs and TECs. (A) LRP-1 mRNA and protein expression in NECs and TECs. Semi-quantitative analysis was also conducted. Data quantification was performed using imageJ software (National Institutes of Health, US). Data represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three-independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. Statistical significances were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). * p < 0.05. (B) Detection of internalized bLF by Western blotting in NECs and TECs at 1, 4, 8, 12, 16, 24, 48 and 72 h after 1.2 μM bLF treatment. (C) LRP-1 expression and bLF internalization by Western blotting in siLRP-1 NECs and TECs at 8 and 24 h after 1.2 μM bLF treatment. (D) Immunoprecipitation of bLF and TRAF6. (E) p-p65 protein levels by Western blotting in NECs and TECs after 0.012, 0.12 and 1.2 μM bLF treatment (a). p-p65 expression level in siTRAF6 transfected TECs with 1.2 μM bLF treatment (b).