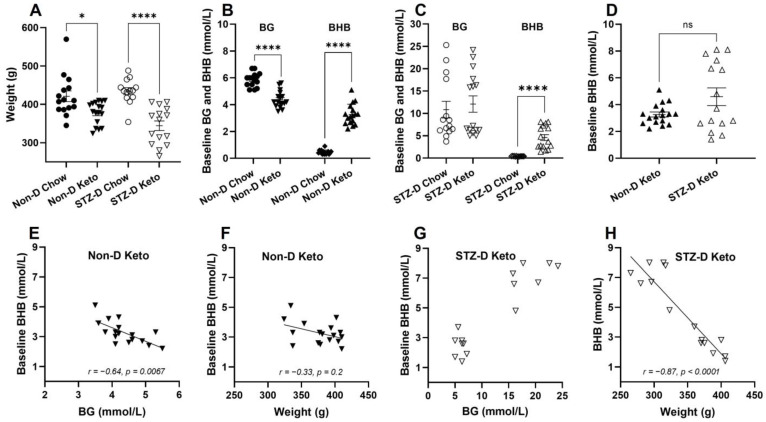
Figure 1.
The effects of three weeks of nutritional ketosis of bodyweight, blood glucose (BG) and β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) of non-diabetic and STZ-diabetic rats. Diabetes was induced with a single i.p. injection of 60 mg/kg STZ (citrate buffer was used in non-diabetic controls), followed by 3 weeks of dietary intervention. (A) Significantly lower bodyweight in ketogenic diet-fed non-diabetic (Non-D Keto) and diabetic (STZ-D Keto) rats compared to respective chow-fed controls; (B) Non-D Keto rats had lower BG and higher BHB concentrations than chow fed controls; (C) Keto diet did not affect BG in STZ-diabetic rats, but significantly elevated BHB; (D) No differences in baseline BHB of Non-D Keto and STZ-D Keto rats were observed; (E) Baseline BHB inversely correlated with BG in Non-D Keto rats; (F) BHB did not significantly correlate with weight in Non-D Keto rats; (G) Highest BHB concentrations in STZ-D Keto rats corresponded to the highest BG; (H) A strong inverse correlation between bodyweight and BHB was detected in STZ-D Keto rats. Data were analysed by Mann–Whitney tests (A–C), Welch’s t-test (D), Spearman’s correlation (E,F). Data shown as mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05, **** p < 0.0001.