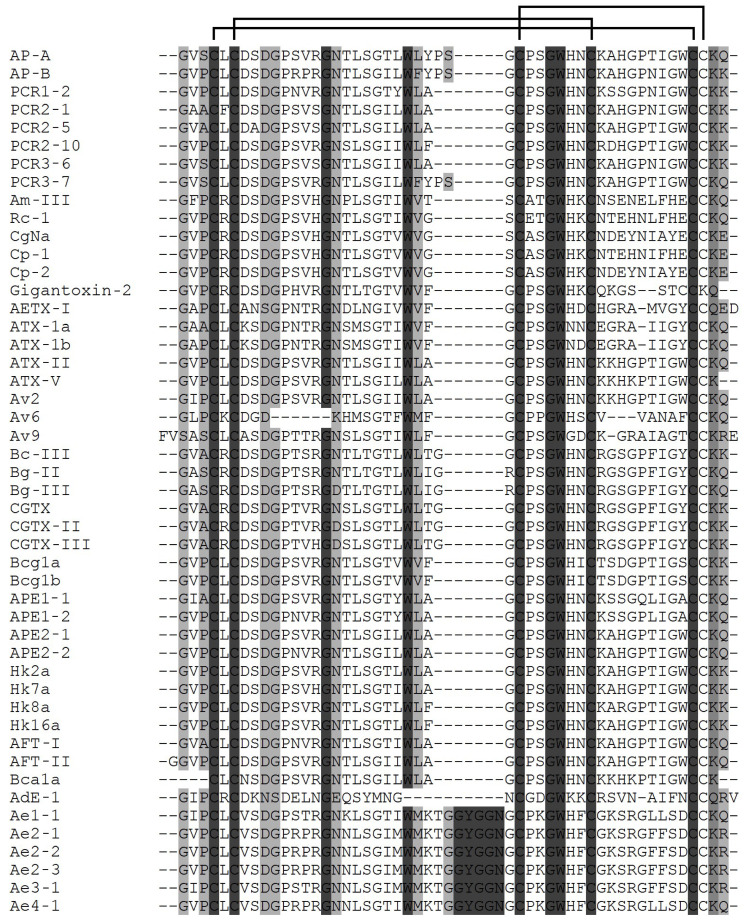
Figure 2.
Multiple alignment of the amino acid sequences of the type 1 sea anemone NaTxs: ApA (UniProt ID: P01530) [25], ApB (P01531) [30], PCR1-2 (P0C5F8), PCR2-1 (P0C5G0), PCR2-5 (P0C5F9), PCR2-10 (P0C5G1), PCR3-6 (P0C5G2), PCR3-7 (P0C5G3) [99] from A. xanthogrammica; Am-III (P69928) [100] from A. maculata; Rc-1 (P0C5G5) [101] from Heteractis crispa (=R. crispus); CgNa (P0C280) [85,102] from C. gigantea; Cp1 (P0CH42) and Cp2 (P0C280) [32] from Condylactis passiflora; Gigantoxin-2 (Q76CA3) [103] from S. gigantea; AETX-1 (P69943) [34] from Anemonia erythraea; ATX-Ia (=ATX-I) (P01533) [96], ATX-Ib (A0A0S1M165), ATX-II (P01528) [23], ATX-V (P01529) [97] from A. sulcata; Av2 (P0DL52) [95,98] from Anemonia viridis (previously known as A. sulcata) and Av6, Av9 (sequences, deduced from A. viridis genomic DNA [95]; BcIII (Q7M425) [104] from B. caissarum; BgII (P0C1F4), BgIII (P0C1F5) [105] from B. granulifera; CGTX (P82803), CGTX-II (P0C7P9), CGTX-III (P0C7Q0) [106], Bcg1a (P86459), Bcg1b (P86460) [107,108] from B. cangicum; APE1-1 (P0C1F0), APE1-2 (P0C1F1) [109], APE2-1 (=ApC) (P01532) [110], APE2-2 (P0C1F3) [109] from Anthopleura elegantissima; Hk2a (P0C5F4), Hk7a (P0C5F5), Hk8a (P0C5F6), Hk16a (P0C5F7) [111] from Anthopleura sp.; AFT-I (P10453), AFT-II (P10454) from Anthopleura fuscoviridis [112]; Bca1a (GenBank accession number: KY789430) [113] from Bunodosoma capense; AdE-1 (E3P6S4) [114] from Aiptasia diaphana; Ae1 (=Ae1-1) (Q9NJQ2) [33] from A. equina, Ae2-1 (B1NWU2), Ae2-2 (B1NWU3), Ae2-3 (B1NWU4), Ae3-1 (B1NWU5), and Ae4-1 (B1NWU6) derived from A. equina genomic DNA [95]. The disulfide bridges are shown above the alignment. The sequence similarity is shown as a dark (high) and light (low) gray background, the multiple sequence alignment was performed using the Vector NTI Advance 11.0 software.