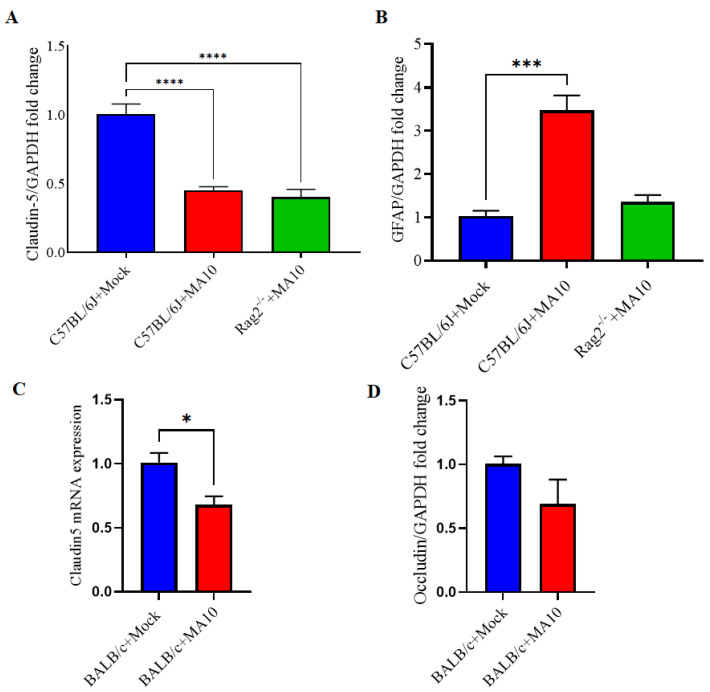
Figure 3.
mRNA expression of Claudin-5 is decreased, and GFAP increased in the brains of mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) infected mice. 10-week-old male C57BL/6J, BALB/c and Rag2−/− mice were inoculated via the intranasal route with mock or MA10 strain of SARS-CoV-2 (1 × 105 TCID50; Red bar). Upon 3 days post-infection (3 dpi), mice were euthanized, and RNA was isolated from the half-left hemisphere of the brain by the Trizol method for gene expression analysis. (A) Claudin-5 and (B) GFAP mRNA expression in brains of mock or SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) infected C57BL/6 mice, whereas (C) Claudin-5 (D) Occludin expression in BALB/c mice were evaluated. Claudin-5 expression was significantly lower in brains of all SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) infected C57BL/6J, BALB/c and Rag2−/− mice compared with C57BL/6J and BALB/c mock-treated mice. GFAP expression was significantly higher in the brains of SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) infected C57BL/6J mice. Occludin expression (D) showed a downtrend in SARS-CoV-2 MA10-infected BALB/c mice compared with mock-treated mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. p values represent mock vs. SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) challenged groups. Significant differences are designated using a two-tailed unpaired student t-test for two groups and one-way ANOVA (for more than two groups). C57BL/6J + Mock n = 5; C57BL/6J + SARS-CoV-2 MA10 n = 5; Rag2−/− + SARS-CoV-2 MA10 n = 5; * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.