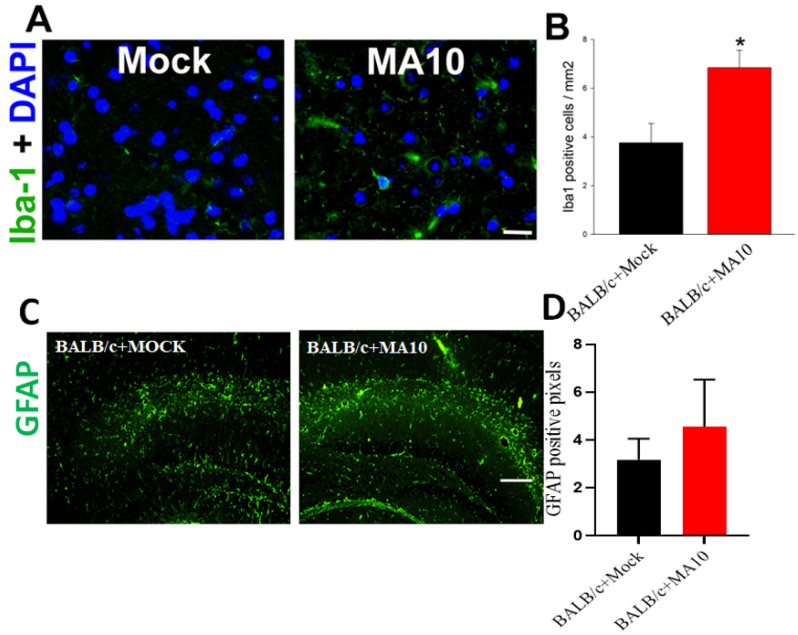
Figure 4.
SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) infection significantly increases Iba-1 positive microglial cells in the cortex region of the brain in 1-year-old female BALB/c mice. 1-year-old female BALB/c mice were inoculated via the intranasal route with saline (black bar) or SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) strain of SARS-CoV-2 (1 × 103 PFU/mL) (Red bar) (Detailed experimental methods are available in Dinnon et al., 2020; Leist et al., 2021). Upon 2 days post-infection (2 dpi), mice were euthanized, and the whole brain was harvested and fixed in 10% phosphate-buffered formalin, paraffin-embedded and sectioned at 4μm thickness. Sequential sections were stained with Iba-1 by immunofluorescence. (A) Representative images of Iba-1 positive microglial cells (Iba1 staining, green) with DAPI as nuclear counterstaining show high induction in the cortex region of brains of SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) infected female BALB/c mice. (B) Quantification of Iba-1 positive microglial cells was significantly higher in SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) infected brains compared with mock infection. SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) infection increases (C,D) GFAP-positive cells in the hippocampus of 12-week old male BALB/c mice after 3 days of infection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. p values represent saline vs SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) challenged groups. Significant differences are designated using a two-tailed unpaired student t-test. Saline n = 5; SARS-CoV-2 MA10 n = 6, * p < 0.01. Scale bar: 40× magnification, scale bar = 25 μm.