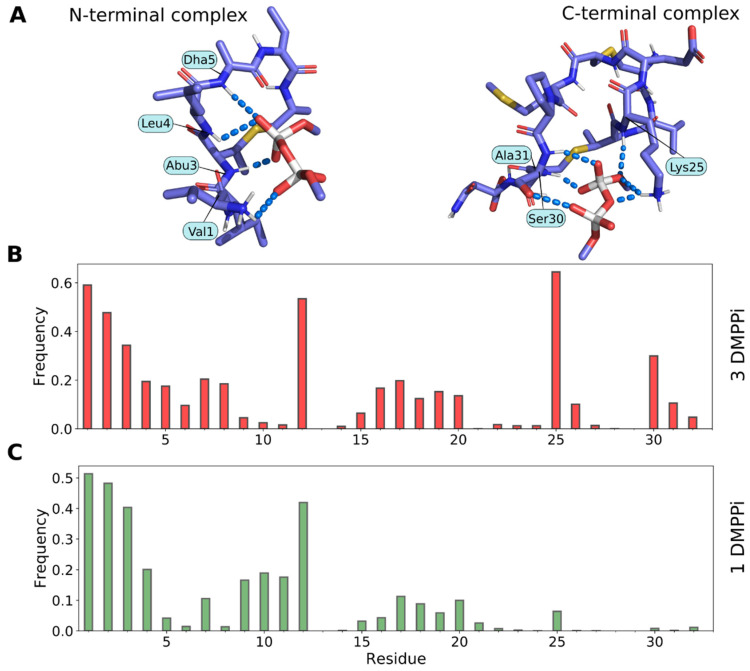
Figure 8.
Molecular modeling reveals both the N- and the C-terminal pyrophosphate recognition sites in Lchα. (A) Representative N-terminal (left) and C-terminal (right) complexes of Lchα with DMPPi, which formed spontaneously during MD simulations. Interacting residues of the peptide are subscribed. (B,C) Per-residue Lchα/DMPPi hydrogen bonding patterns observed in MD trajectories containing three (B) or one (C) DMPPi ion. Bar height is the lifetime of the hydrogen bond between a given residue and DMPPi as a fraction of the MD time (estimated based on five 500-ns trajectories). Note that the C-terminal site is active only when the N-terminal site is already occupied (upon DMPPi excess). Data are given for the full-length Lchα; similar results were obtained for the N-terminal Lchα1–21 and C-terminal Lchα22–32 fragments (data not shown). Please note that the N-terminal 2-oxobutyryl group was replaced with the valine residue.