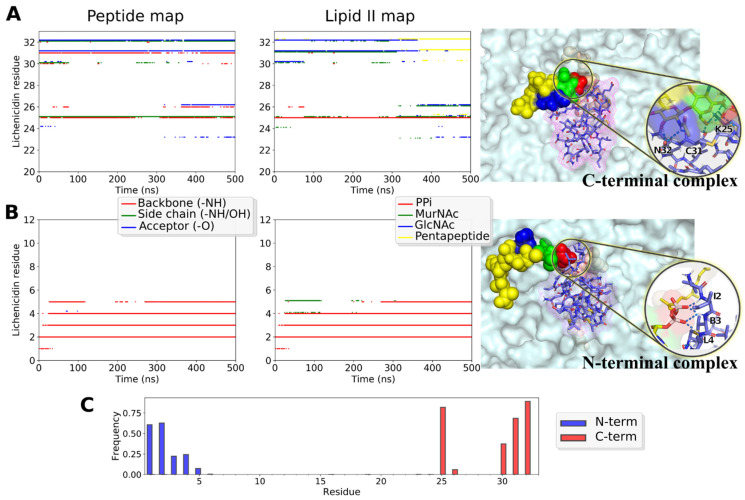
Figure 9.
Structure and dynamics of the predicted C- and N-terminal complexes of the full-length Lchα with lipid II in the model bacterial membrane. (A,B) Intermolecular interactions and the snapshot of the complexes’ structure from MD simulations. Left and Middle panels: intermolecular hydrogen bonding maps that describe complex organization and dynamics. Left panel: peptide groups taking part in h-bond formation at a certain MD time: backbone amide group that donates the proton (red dots), side chains (green), and backbone carbonyl group, which accepts the proton (blue). Middle panel: the lipid II groups forming the same h-bonds: PPi (red), MurNAc sugar (green), GlcNAc sugar (blue), and the pentapeptide (yellow). Right panel: the representative snapshot from MD. Lipid II is color-coded as in the middle panel. The membrane is shown with the surface. Interactions are zoomed in the inset. (A) C-terminal complex involves the peptide side chain. Note that we obtained several unlike modes of the C-terminal complex, relatively stable in MD (Figure S10). (B) The N-terminal complex, in a nisin-like manner, is based exclusively on the backbone amide protons interactions with the pyrophosphate moiety. (C) Lchα residues involvement into the N- (blue) and C-terminal (red) complexes, as shown with h-bonds lifetime (as a fraction of cumulative time of MD sets).