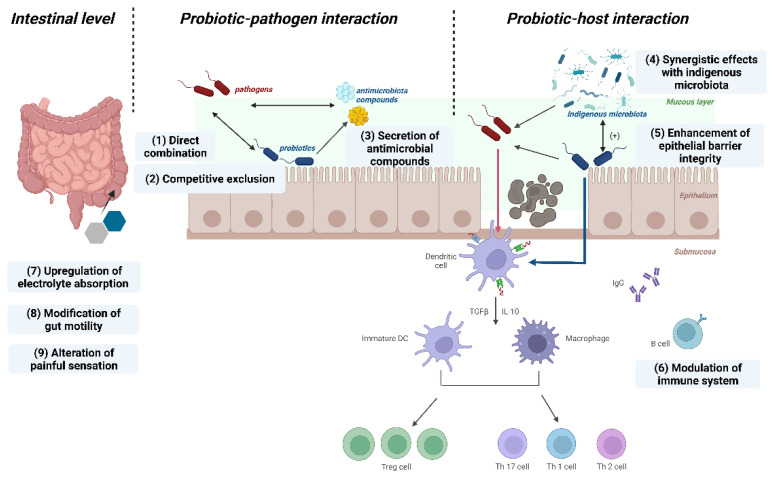
Figure 1.
Predominant mechanisms of probiotic action. Probiotic-pathogen interactions in the middle part of the figure include three mechanisms: (1) direct combination, (2) competitive exclusion, (3) secretion of antimicrobial compounds; Probiotic-host interactions in the right part of the figure include three mechanisms: (4) synergistic effects with indigenous microbiota, (5) enhancement of epithelial barrier integrity, (6) modulation of immune system. At the intestinal level in the left part of the figure, probiotics have an effect through: (7) upregulation of electrolyte absorption, (8) modulation of gut motility, (9) alteration of painful sensations. (Figure was created with Biorender. com).