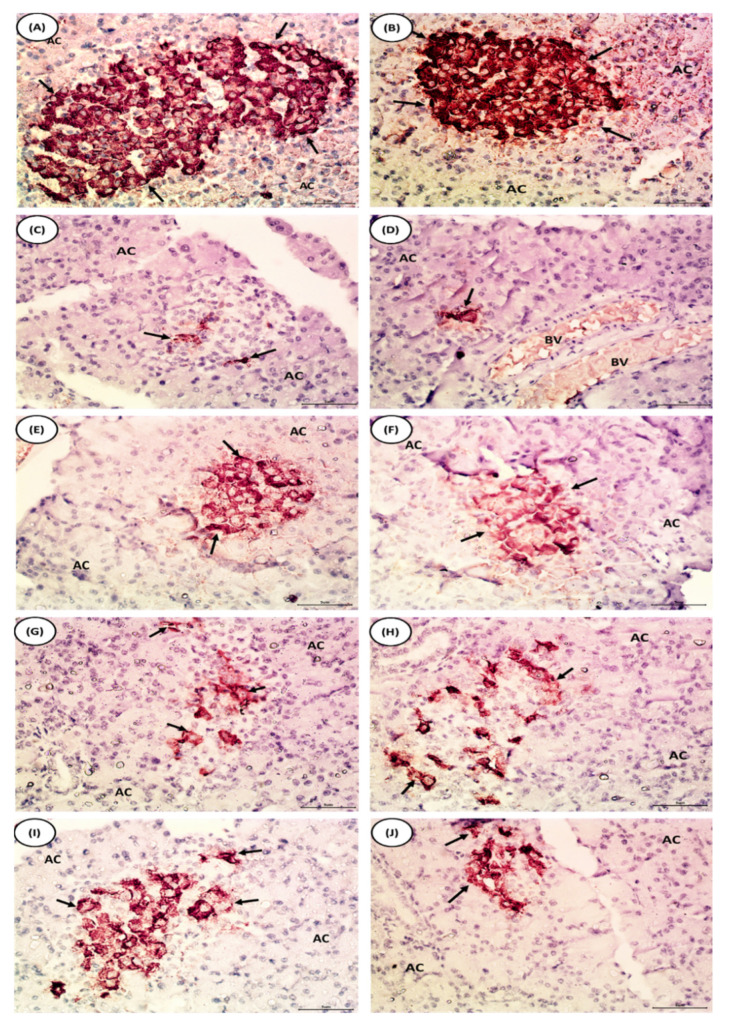
Figure 7.
Photomicrographs of immunohistochemical staining of insulin in pancreatic islets of the normal, diabetic control, and diabetic treated rats. (A,B) Pancreas section of rats from normal group showing strong immunoreactivity of insulin in β-cells which are distributed over the pancreatic islets (arrows) and stained with deep brown color. (C,D) Pancreas section of rats from NA/STZ-induced diabetic group showing evident decline in the immunohistochemical expression of insulin in islet of Langerhans (arrows). (E,F) In the pancreas of diabetic rats treated with chrysin, the apparent marked increase in number and area of β-cells with dense immunohistochemical staining of insulin granules is evident in comparison with NA/STZ-induced diabetic group (arrows). (G,H) Pancreas section of rats treated with BM-MSCs showing an evident increase in insulin expressing β-cells (arrows). (I,J) In the pancreas of diabetic group rats treated with chrysin plus BM-MSCs, the apparent marked increase in number and area of β-cells is evident in comparison with NA/STZ-induced diabetic group (arrows).