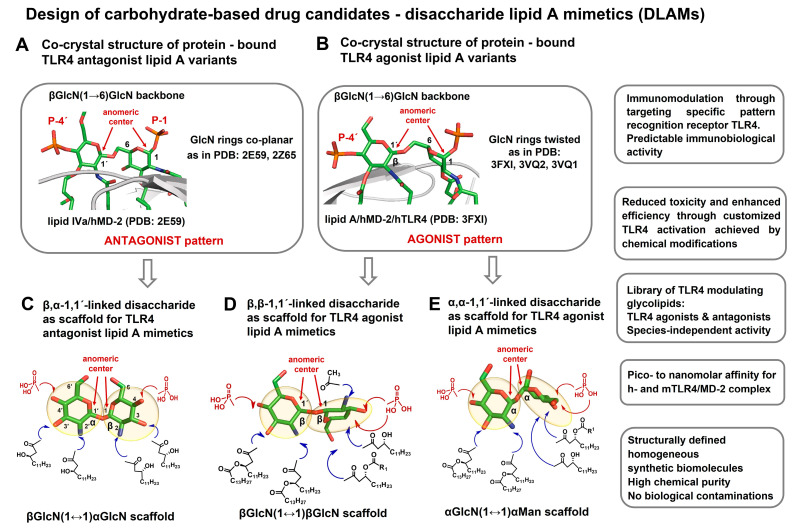
Figure 6.
Co-crystal-structure-based design of disaccharide lipid A mimetics (DLAMs). (A) The co-crystal structures of hMD-2-bound lipid IVa and Eritoran (PDB codes: 2E59 and 2Z65, respectively) disclose a co-planar relative orientation of two GlcN rings comprising the β(1→6)-linked diglucosamine backbone of lipid A. This arrangement is achieved through rotation about flexible β(1→6) linkage. A specific co-planar relative orientation of the GlcN rings in a βGlcN(1→6)GlcN backbone in a protein-bound lipid A is designated an “antagonist pattern”. (B) The co-crystal structures of hMD-2/TLR4-bound E. coli lipid A (PDB code: 3FXI), mMD-2/TLR4-bound E. coli lipid A (PDB code: 3VQ2), and mMD-2/TLR4-bound lipid IVa (PDB code: 3VQ1) reveal a skewed relative orientation of two GlcN rings in the β(1→6)-linked diglucosamine backbone of protein-bound lipid A. This relative orientation of GlcN rings achieved through rotation about β(1→6) linkage is designated an “agonist pattern”. (C) Design of TLR4 antagonist lipid A mimetics. The co-planar molecular shape of β,α-1,1´-linked diglucosamine mirrors the 3D-topology of the βGlcN(1→6)GlcN backbone of hMD-2-bound TLR4 antagonists shown in (A). The sites of attachment of the lipid chains and phosphate groups for the synthesis of lipid A mimetics are represented by blue and red arrows, respectively. (D) Design of TLR4 agonist lipid A mimetics based on a β,β-1,1´-diglucosamine scaffold. The 3D-structure of a synthetic β,β-(1↔1´)-linked diglucosamine scaffold with two GlcN rings in a twisted relative orientation. The sites of possible chemical attachment of functional groups are indicated by arrows: the acylation/phosphorylation pattern of the distal GlcN ring corresponds to that of E. coli LPS, whereas the proximal GlcN ring has a variable acylation and phosphorylation pattern. (E) Design of TLR4 agonist lipid A mimetics based on an α,α -1,1´-linked disaccharide scaffold. The skewed molecular shape of an α,α-1,1´-linked diglucosamine mirrors the 3D-topology of a βGlcN(1→6)GlcN backbone of MD-2-bound TLR4 agonists shown in (B). The acylation and phosphorylation pattern of the distal GlcN ring corresponds to that of E. coli lipid A, whereas the proximal pyranose ring (Man) entails variable acylation and phosphorylation pattern. The sites of possible attachment of lipid chains are shown by blue arrows; the sites proposed for chemical phosphorylation are shown by red arrows. Images were generated with PyMol.