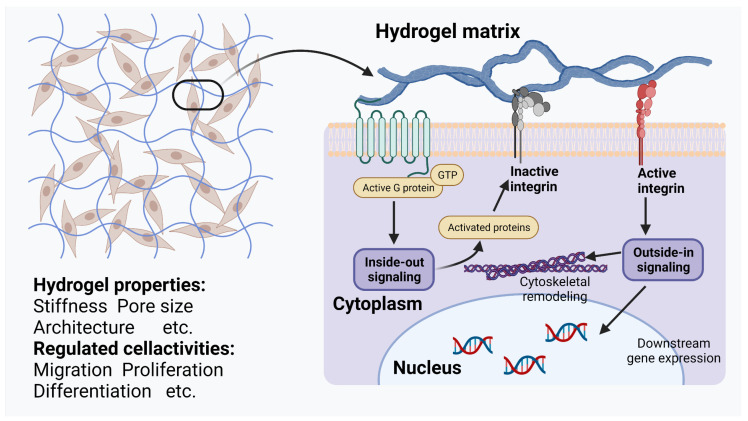
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the communication between hydrogel and the cell. Modulation of various modifiable physicochemical properties of the hydrogel can act on cell surface receptors (such as α1β1 and α2β1 integrins [23] and CD44 [24], and depends on the type and physicochemical properties of the hydrogel) and thereby modulate intracellular signal transduction pathways (such as STAT3 [24]). This figure was created with BioRender, accessed on 1 December 2022 (https://biorender.com/).