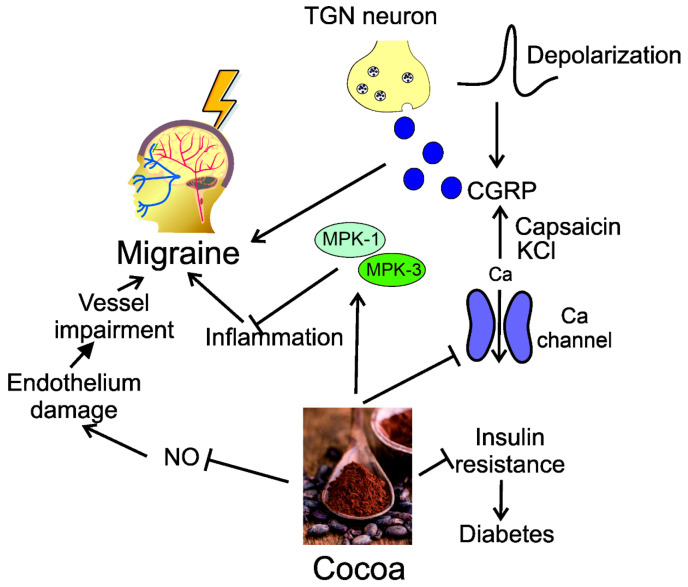
Figure 2.
Cocoa is an example of a natural dietary nutrient that may exert beneficial effects against migraine, which may be partly underlined by its interaction with calcitonin-related gene peptide (CGRP) and represents mechanisms that may underline the action of other dietary nutrients on migraine and the CGRP systems. CGRP may be released after the depolarization of trigeminal nerve (TGN) neurons with the involvement of calcium signaling. Cocoa may disrupt calcium channels resulting in changing CGRP release, mediated by capsaicin and KCl. Cocoa may directly inhibit NO production, decreasing vessel impairment underlined by NO-induced endothelial damage. Coca may upregulate mitogen-activated kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and -3, which exert an anti-inflammatory effect, which is important in migraine prevention. Cocoa is also reported to break insulin resistance preventing diabetes, whose connection with migraine is discussed further in the main text.