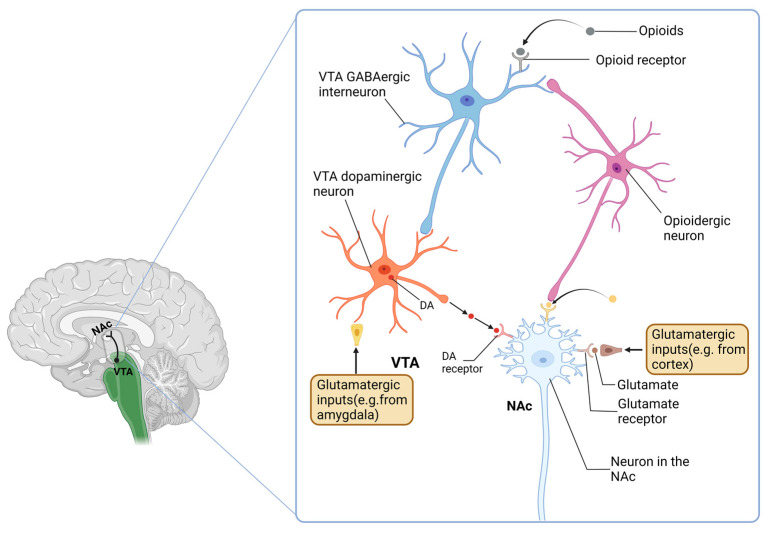
Figure 3.
Rewarding actions of opioids in the VTA and NAc. Drug abuse, especially opioid abuse, has some significant effects on the area of VTA and NAc. γ -aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic interneurons in the VTA are inhibited by opioids mainly via μ-opioid receptors but also by δ-opioid receptors. This leads to the disinhibition of VTA dopaminergic neurons and activation of reward circuitry in the Nac. Furthermore, reward circuitry is also activated directly by opioids through opioid receptors on NAc neurons. VTA: ventral tegmental area; NAc: nucleus accumbens.