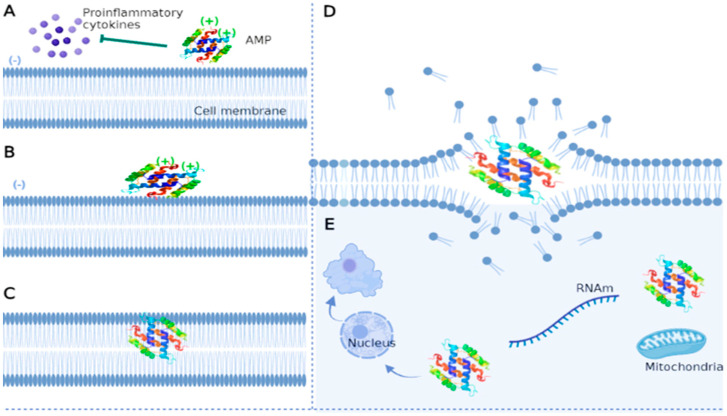
Figure 2.
Main mechanisms of action of antifungal peptides. (A)—AMPs can play immunomodulatory roles by inhibiting the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor. (B)—AMPs interact with the fungal membrane through electrostatic interactions due to charge differences (negatively charged membrane and positively charged peptide). (C)—The hydrophobic character of AMP enables its insertion into the membrane through a perpendicular orientation as its concentration increases. (D)—AMPs dislocate lipids and destroy the membrane. (E)—The peptide can enter the cell and damage various structures such as the nucleus, inhibit RNA synthesis, attack mitochondria, and induce functional alterations up to cell death. The figure was created with https://app.biorender.com.