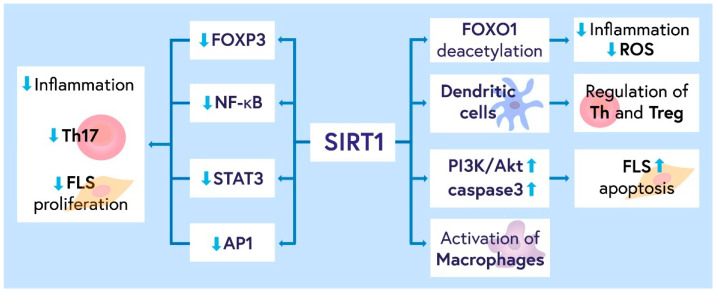
Figure 1.
The role of SIRT1 in RA and other autoimmune diseases. SIRT1 could decrease inflammation by inhibiting transcriptional factors such as NF-κB, STAT3, AP-1, FoxP3, FOXO1 deacetylation, and macrophage activity inhibition. By regulating dendritic cells, SIRT1 could control the response mediated by Th and Treg cells. The FLs proliferation and apoptosis are controlled by SIRT1 activity through PI3K/Akt, caspase 3, and NF-κB pathways. Abbreviations: FLs, synoviocytes fibroblasts; AP1, activator protein 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Th, T helper cells; Treg, T regulatory cells; Th17, T helper 17 cells; FOX, forkhead box; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; PI3K/Akt, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway; SIRT1, sirtuin 1.