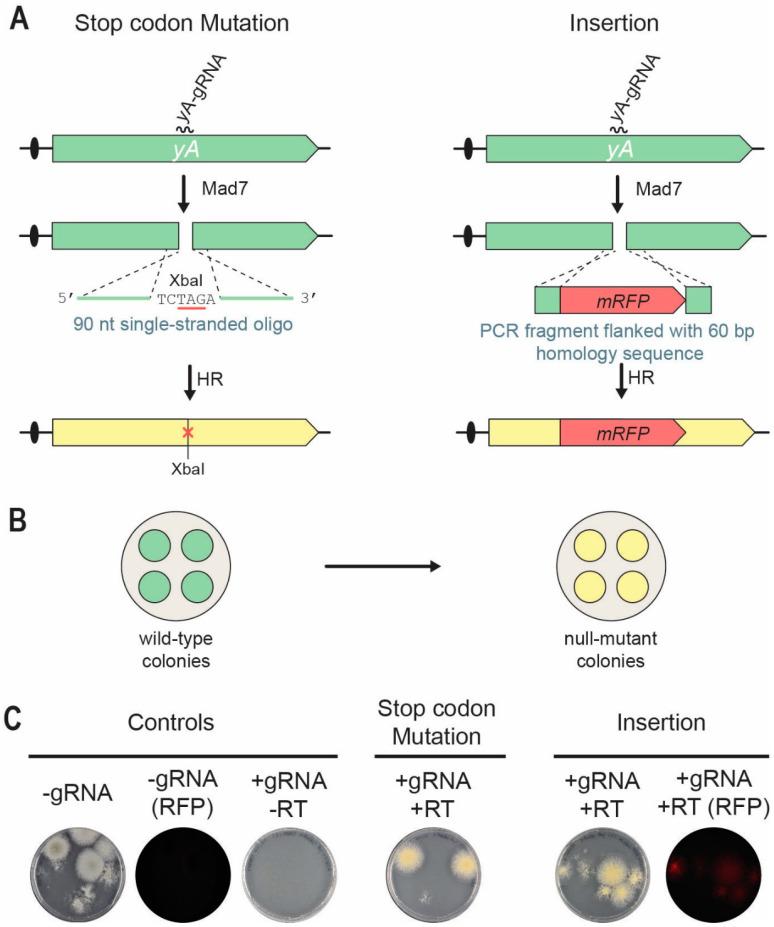
Figure 2.
Mad7-induced gene editing of the yA locus in A. nidulans. (A) Strategies for introducing a specific stop-codon/XbaI mutation (left) and an mRFP insertion (right) into yA. A DNA DSB is introduced in yA by the Mad7/yA-gRNA CRISPR nuclease. A single-stranded oligonucleotide is used as RT to direct introduction of stop-codon/XbaI mutation into yA by homologous recombination (HR). A PCR fragment is used as RT to direct insertion of mRFP into yA by HR. See main text for further details. (B) Mutation of yA changes the conidia color of transformants growing on solid medium from wild-type green to yellow. (C) To the left, transformation controls with empty Mad7-CRISPR plasmid (pDIV298) images in visible or in red fluorescent light (RFP); and with the yA-Mad7-CRISPR plasmid (pDIV711) in the absence of a RT. In the middle, introduction of the stop-codon/XbaI mutation into yA by co-transforming A. nidulans with pDIV711 and a single-stranded oligonucleotide (PR_DIV3197) serving as RT. RT mediated repair introduces an XbaI site and an amber stop codon. To the right, insertion of mRFP into yA by co-transforming A. nidulans with plasmid (pDIV711) and a mRFP-PCR fragment serving as RT.