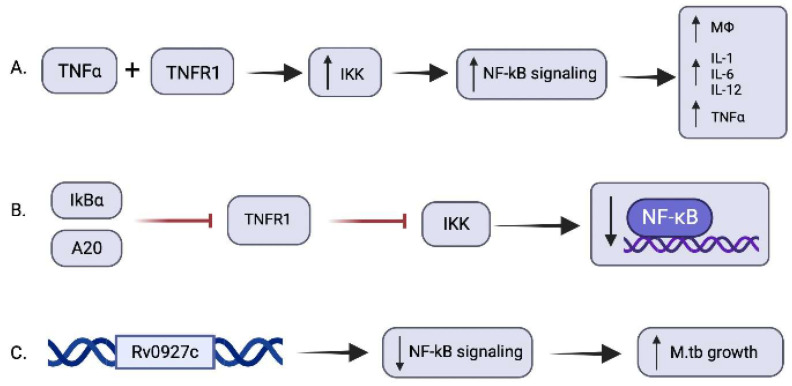
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways revolving around NF-κB and the effect of M. tb. (A) TNF-α binds with TNFR1 to activate IκB kinase leading to increased free NF-κB signaling to produce various pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, TNF-α, and activated macrophages. (B) The additional products of NF-κB containing IκBα and A20 result in the inhibition of TNFRI, an activator of IKK. The inhibition of TNFR1 and the subsequent inhibition of IKK leads to a decrease in NF-κB. (C) The Rv0927c gene activated during an M. tb infection reduces NF-κB signaling and, in turn, increases M. tb growth and survival as a result.