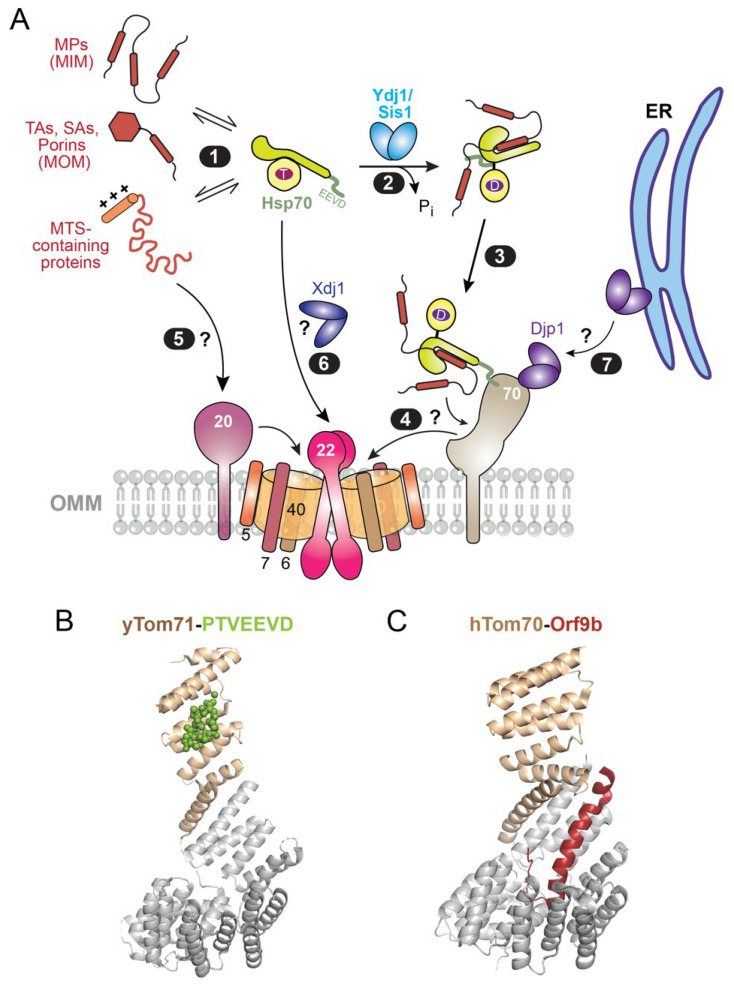
Figure 5.
Role of Hsp70 in protein targeting to mitochondria. (A) Potential cytosolic events during the targeting of mitochondrial proteins. Diverse mitochondrial proteins with distinct targeting signals and biophysical properties are captured by Hsp70, likely with assistance of JDPs (steps 1–2). Substrate-loaded Hsp70 can associate with the Tom70 receptor on the mitochondria surface via interaction of its EEVD motif with the N-terminal TPR domain of Tom70 (step 3). Hsp70-bound substrates might be transferred to the preprotein-binding groove on Tom70 or directly to the core TOM complex (step 4). MTS-containing precursor proteins are preferentially captured by the Tom20 receptor (path 5). The JDP Xdj1 specifically associates with Tom22 in the core TOM complex and assists in mitochondrial protein import in an Hsp70-dependent manner, the mechanism of which is unclear (path 6). Additionally, the JDP Djp1 specifically binds Tom70 and is important for the biogenesis of Mim1; it is unclear whether this role of Djp1 is related to its ability to retrieve mitochondrial proteins localized to the ER membrane (path 7). (B) The crystal structure of Tom71 cytosolic domain bound to the Hsp70 C-terminal peptide (lime; PDB 3fp4). The N- and C-terminal subdomains of Tom71 are in tan and grey, respectively. (C) The crystal structure of human Tom70 bound to the Orf9b peptide (brick; PDB 7dhg). Domain coloring is the same as in (B).