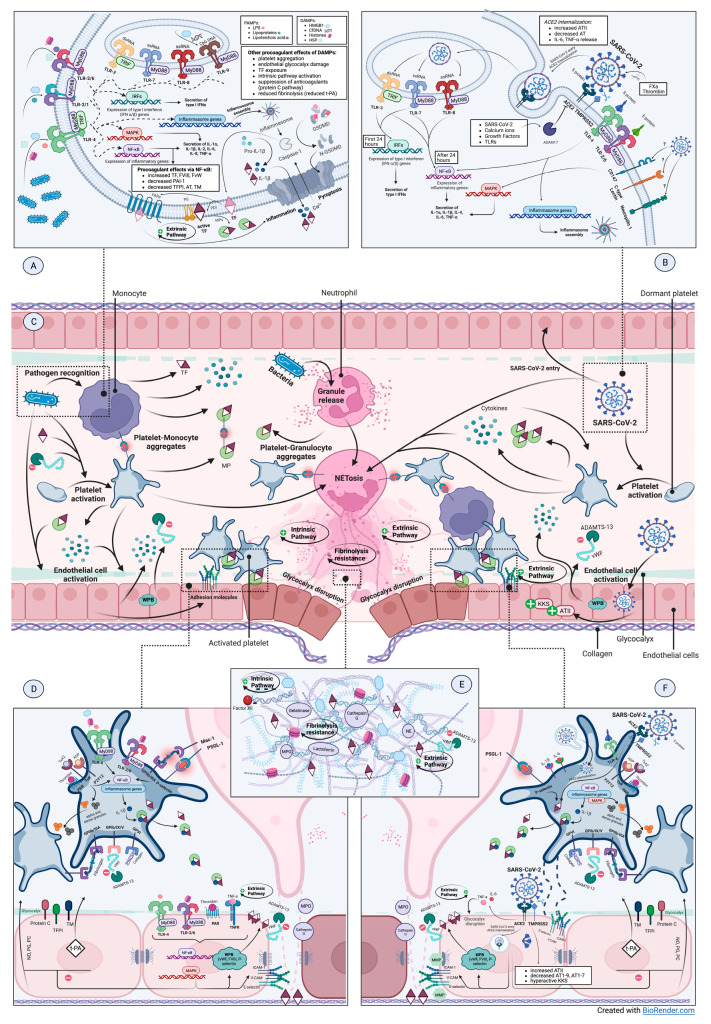
Figure 1.
A comparative overview of pathogenic mechanisms involved in sepsis-induced coagulopathy and COVID-19-associated coagulopathy. (A). Pathogen recognition pathways in bacterial sepsis. (B). Molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry and subsequent cell injury. (C). Intravascular interplay of pathogens (i.e., bacteria and SARS-CoV-2), effector cells and humoral factors in the context of sepsis-induced coagulopathy versus COVID-19-associated coagulopathy. (D). Platelet and endothelium dysfunctions in bacterial sepsis. (E). NETs components and NET-associated prothrombotic status. (F). Platelet and endothelium dysfunctions in COVID-19. Abbreviations: ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ADAM17, a disintegrin and metalloprotease 17; ADAMTS13, a disintegrin and metalloprotease with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AT, antithrombin; ATII/1-9/1-7, angiotensin II/1-9/1-7; CD147, cluster of differentiation 147; Cf/CpG DNA, cell-free/cytosine-guanine pair desoxyribonucleic acid; CLR, C-type lectin receptor; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; FVIII/X/XII, coagulation factor VIII/X/XII; GP-Iba-IX-V, glycoprotein Iba-IX-V; GPIIb/IIIa, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa; GPVI, glycoprotein VI; GSDMD, Gasdermin D; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; Hsp, heat-shock proteins; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; IRF, interferon-regulatory factor; KKS, kallikrein-kinin system; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; Mac-1, macrophage 1 antigen; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP, matrix metalloprotease; MP, microparticle; MPO, myeloperoxidase; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NE, neutrophil elastase; NET, neutrophil extracellular trap; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NO, nitric oxide; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; PAR, protease-activated receptor; PC, prostacyclin; PDI, protein disulfide isomerase; PG, prostaglandin; PS, phosphatidyl-serine; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; ss/dsRNA, single-stranded/double-stranded ribonucleic acid; TF, tissue factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TM, thrombomodulin; TMPRSS2, transmembrane protease serine 2; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α TNFR, TNF receptor; t-PA, tissue-type plasminogen activator; TRIF, toll-interleukin 1 receptor-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-beta; TxA2, thromboxane A2; TxR, thromboxane receptor; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; vWF, von Willebrand Factor; WPB, Weibel Palade Bodies.