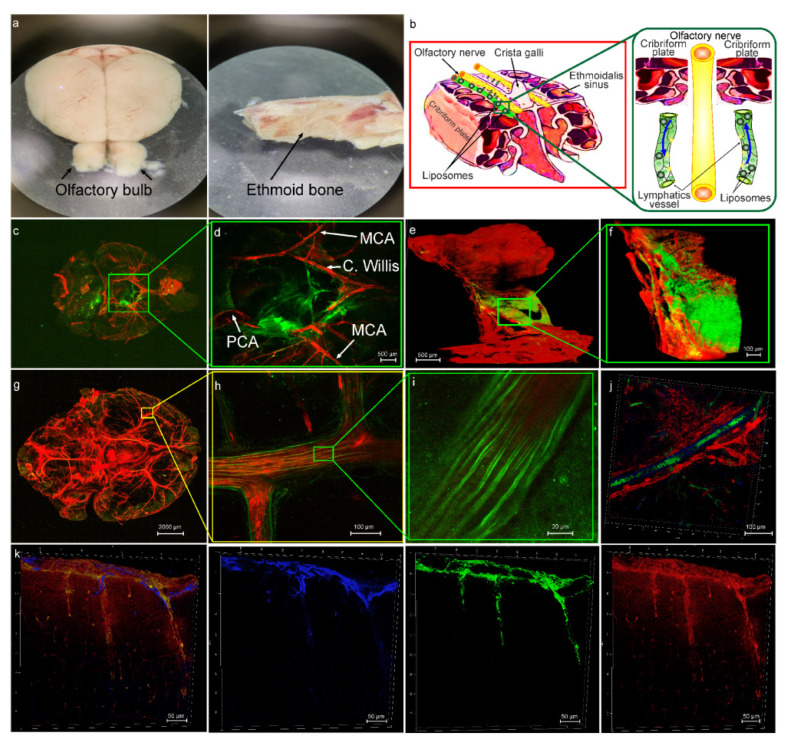
Figure 1.
The lymphatic pathway of delivery of liposomes (green) to mouse brain from the HG group: (a) Images of the ethmoid bone and the olfactory bulb, which were used for confocal and multiphoton imaging of distribution of liposomes after its intranasal injection; (b) schematic illustration of hypothesis that after intranasal administration, liposomes with the extracellular fluids enter the lumen of LVs in the nasal mucosa and are drained in both directions, from and into the brain via the space between the OSN providing directed fluid flow; (c) representative confocal image of ventral part of the brain after intranasal injection of liposomes (green), the cerebral vessels were filled with the Evans Blue dye (red, i.v.); (d) representative confocal image of region of interest from (c), the image shows distribution of liposomes (green) along the main arterial vessels: MCA: middle cerebral artery, C. Willis: Circle of Willis, PCA: posterior cerebral artery; (e)—multiphoton image of the cribriform plate immersed in buffer solution and covered with cover glass. Objective—10 × 0.45, two photon fluorescence excitation 970 nm, emission: green (liposomes) 506—593 nm; red (Evans Blue) 604—679 nm; (f) multiphoton image of region of interest from (e), the image demonstrates distribution of liposomes (green) in the freshly removed cribriform plate stained with Evans Blue (red, emission 604—679 nm); (g) whole imaging of the mouse brain after intranasal delivery of liposomes; (h,i) the region of the middle cerebral artery (red, filled with Evans Blue) depicting directional distribution of liposomes; (j) the presence of liposomes (green) in the MLVs labeled with Live-1 (blue), the blood vessels (red) filled with Evans Blue; (k) representative images of distribution of liposomes (green) along the brain surface, astrocytes are labeled with GFAP (blue), the cerebral blood vessels were filled with Evans Blue (red).