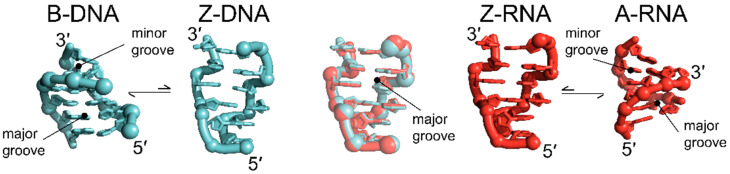
Figure 1.
Z-DNA and Z-RNA are structurally equivalent. Although the right-handed B- (left, cyan, PDB: 1N1K [24]) and A-conformations (right, red, PDB: 1PBM [25]) of helical DNA and RNA are structurally distinct from each other, they can both adopt the left-handed Z-conformation (middle, PDBs: 1QBJ [7] for DNA and 2GXB [10] for RNA). Unlike the phosphate backbones of A- and B-conformation nucleic acids, which follow a smooth curve, the backbone of the Z-conformation zig-zags. Overall, the helical parameters of Z-DNA and Z-RNA are very similar (Table 1), with the opening of the minor groove of Z-RNA only being marginally smaller than that of Z-DNA.