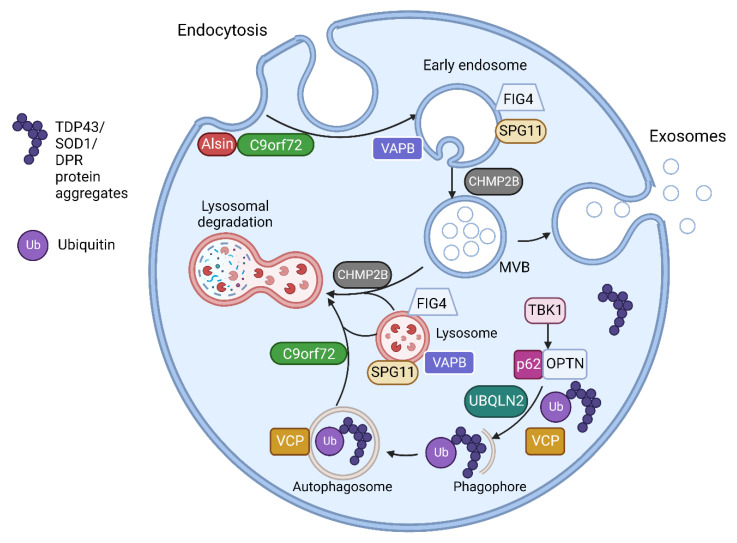
Figure 2.
The endosomal and vesicular pathway involvement of proteins encoded by ALS related genes. Alsin activates Rab5 to promote endosomal fusion and subsequent endosomal trafficking. C9orf72 forms a complex with SMCR8 (Smith-Magenis Syndrome Chromosome Region, Candidate 8) and WDR41 (WD Repeat domain 41) proteins. This complex interacts with Rab GTPases including Rab5 in endosomal formation and trafficking. The C9orf72 complex also regulates various steps in autophagy including MVB-autophagosome and autophagosome-lysosome fusion as well as regulating several aspects of lysosomal biogenesis, pH and reformation. VAPB encodes Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C found in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This anchors complexes involved in lipid transfer from the ER to golgi and also the recycling of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PtdIns4P). VAPB mutations disrupt ER-golgi tethering and leads to PtdIns4P accumulation with subsequent accumulation of endosomes and dysfunctional lysosomes. FIG4 is required for the homeostasis of a signalling lipid phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate (PI(3,5)P2), which is required for endosomal and lysosomal maturation. FIG4 mutations result in enlarged endosomes and lysosomes with impaired lysosomal function. CHMP2B is responsible for the formation of intraluminal vesicles within the MVBs and may participate in the proper fusion of MVB with the lysosomes and the autophagosomes. CHMP2Bintron5 mutation results in accumulation of large endosomes and autophagosomes. VCP is involved in the initiation of autophagy and autophagosome maturation. TBK1 phosphorylates both optineurin (OPTN) and Sequestosome-1/p62, increasing their ability to bind to ubiquitinated cargo, initiating autophagy and delivery to autophagosomes. UBQLN2 interacts with LC3, a marker for starvation induced autophagy, to deliver ubiquitinated cargo to autophagosomes and is also recruited to OPTN containing vesicles. Spatacsin interacts with Rab5 for endosomal trafficking and maturation and contributes to lipid clearance from late endosomes and lysosomes. SPG11 mutations result in loss of spatacsin function, which leads to accumulation of lipids in lysosomes. Figure created using Biorender.com.