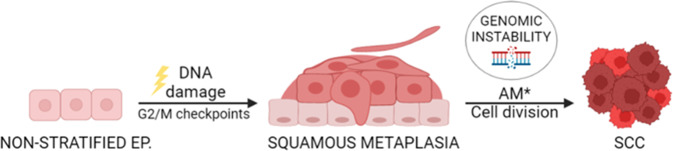
Fig. 7. Model for the role of DNA-damage and mitotic checkpoints in the development of squamous metaplasia and subsequent squamous cancer in non-stratified epithelia.
Chronic or acute exposure of non-squamous epithelia to genotoxic agents would drive G2/M arrest via the DNA damage response. In turn, G2/M checkpoints would drive benign hyperplastic squamous differentiation (squamous metaplasia). Unrepaired cells would undergo terminal post-mitotic squamous differentiation. In the event of additional mutations (AM) hitting the G2/M checkpoints, cells overcoming the cell division block would proliferate bearing genomic instability, eventually resulting in cancer. Ep: epithelium. Created with BioRender.com.