Figure 1.
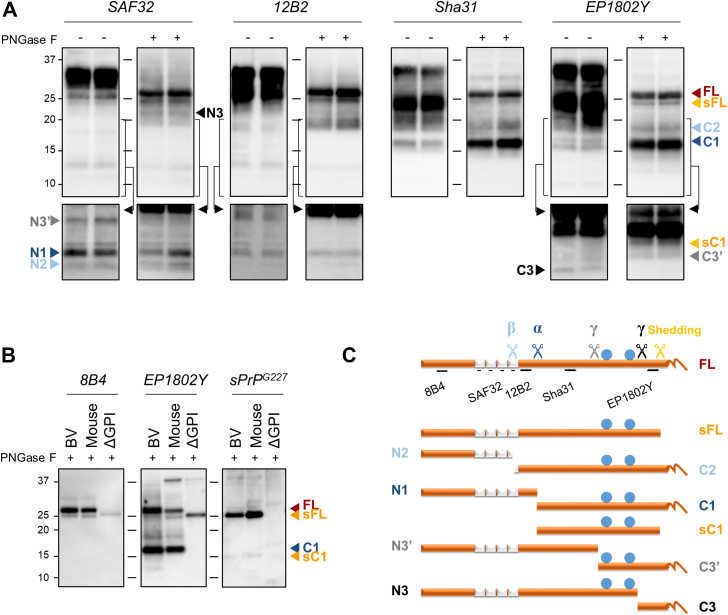
Identification and schematic representation of bank vole PrPCproteoforms derived by endoproteolytic processing.A, representative Western blots of brain homogenates prepared from two healthy bank voles subjected to PNGase F treatment (+, right blot of each pair) or left untreated (−, left blot of each pair). Replica blots were probed with different antibodies (Abs), indicated at the top of each pair of blots. PrPC proteoforms are indicated with colored arrowheads: orange is used for PrPC proteoforms derived by shedding (shed full length [sFL] and shed C1 [sC1]), blue and light blue for PrPC fragments derived by α- (N1/C1) and β-cleavages (N2/C2), and gray and black for PrPC fragments derived by γ-cleavage (N3′/C3′ and C3/N3). A red arrowhead indicates full-length PrPC (FL). Note that deglycosylation (+samples) was necessary to detect the glycosylated proteoforms of PrPC (FL, C1, C2, sFL, sC1, C3′, and N3), whereas nonglycosylated fragments were more easily detected in untreated samples (N1, N2, N3′, and C3). A long exposure of the same blots (black arrow, the bracket indicates the portion of the blots shown after a longer exposure) was necessary for a clearer identification of less abundant PrPC fragments. Tissue equivalents (TEs) loaded per lane were 0.2 mg for untreated (−) and 0.06 mg for PNGase F-treated (+) samples. The positions of molecular weight (MW) markers are indicated as black lines between “PNGase −“ and “+” blots, whereas the respective kilodaltons are reported on the left of the first blot. B, representative Western blots of PNGase F-treated brain homogenates from bank vole, WT mouse, and tgBVΔGPI. Replica blots were probed with the extreme N-terminal (8B4, first blot of the panel), extreme C-terminal (EP1802Y, second blot of the panel), and mouse shed PrP-specific (sPrPG227, third blot of the panel) antibodies. The latter (sPrPG227) detected a fragment with an apparent MW of approximately 25 kDa in both mouse and bank vole PNGase F, that is, sFL (higher orange arrowhead). EP1802Y and 8B4 detected the same fragment, few kilodaltons below FL (red arrowhead). The sPrPG227 antibody detected another fragment of approximately 14 kDa, that is, shed C1 (sC1), also recognized, few kilodaltons below C1 (blue arrowhead), by EP1802Y (lower orange arrowhead). TE loaded per lane were 0.06 mg for bank vole and WT mouse samples and 0.12 mg for tgBVΔGPI. The positions of MW markers are indicated as black lines between the blots, whereas the respective kilodaltons are reported on the left of the first one. C, linear representation of PrPC (23–231) showing (i) the octarepeat region (repeated white boxes); (ii) the N-glycosylation sites (blue spheres, amino acids 181 and 197); (iii) the GPI-anchor (curved line, extreme C terminus); (iv) epitopes of pan-PrP antibodies used herein. Colored scissors indicate the main cleavage events and the respective cleavage products reported below. β-cleavage (light blue scissors) occurs at multiple sites at the end of the octarepeat domain of PrPC, around amino acid 90, and produces the soluble N-terminal N2 fragment of ∼10 kDa and the membrane-bound C-terminal fragment C2 (∼18 kDa). The major cleavage event, termed α-cleavage (blue scissors), occurs between residues H109 and K110 and produces the soluble N-terminal fragment N1 (∼12 kDa) and the ∼16 kDa C-terminal membrane anchored fragment C1. Shedding (orange scissors) occurs at the extreme C terminus of PrPC resulting in the release of almost full-length PrPC, that is, sFL (∼25 kDa), or almost full-length C1 fragment, that is, sC1 (∼14 kDa), from the plasma membrane. Finally, γ-cleavage (gray and black scissors) occurs in the C-terminal region of PrPC, between amino acids 170 and 200. Our data indicate the presence of two “γ-cleavage-like sites,” one occurring N-terminal to the first N-glycosylation site (gray scissors) and producing the nonglycosylated soluble N-terminal fragment N3′ (∼17 kDa) and the ∼10 kDa glycosylated membrane-bound C3′, one occurring more C-terminally (black scissors), after the second N-glycosylation site, producing the ∼20 kDa glycosylated soluble N-terminal fragment N3 and the C-terminal nonglycosylated fragment C3 (∼7 kDa). PrPC, cellular prion protein.; sC1, shed C1; sFL, shed FL-PrPC.