Figure 2. Methods used for analysis of neuronal genome editing.
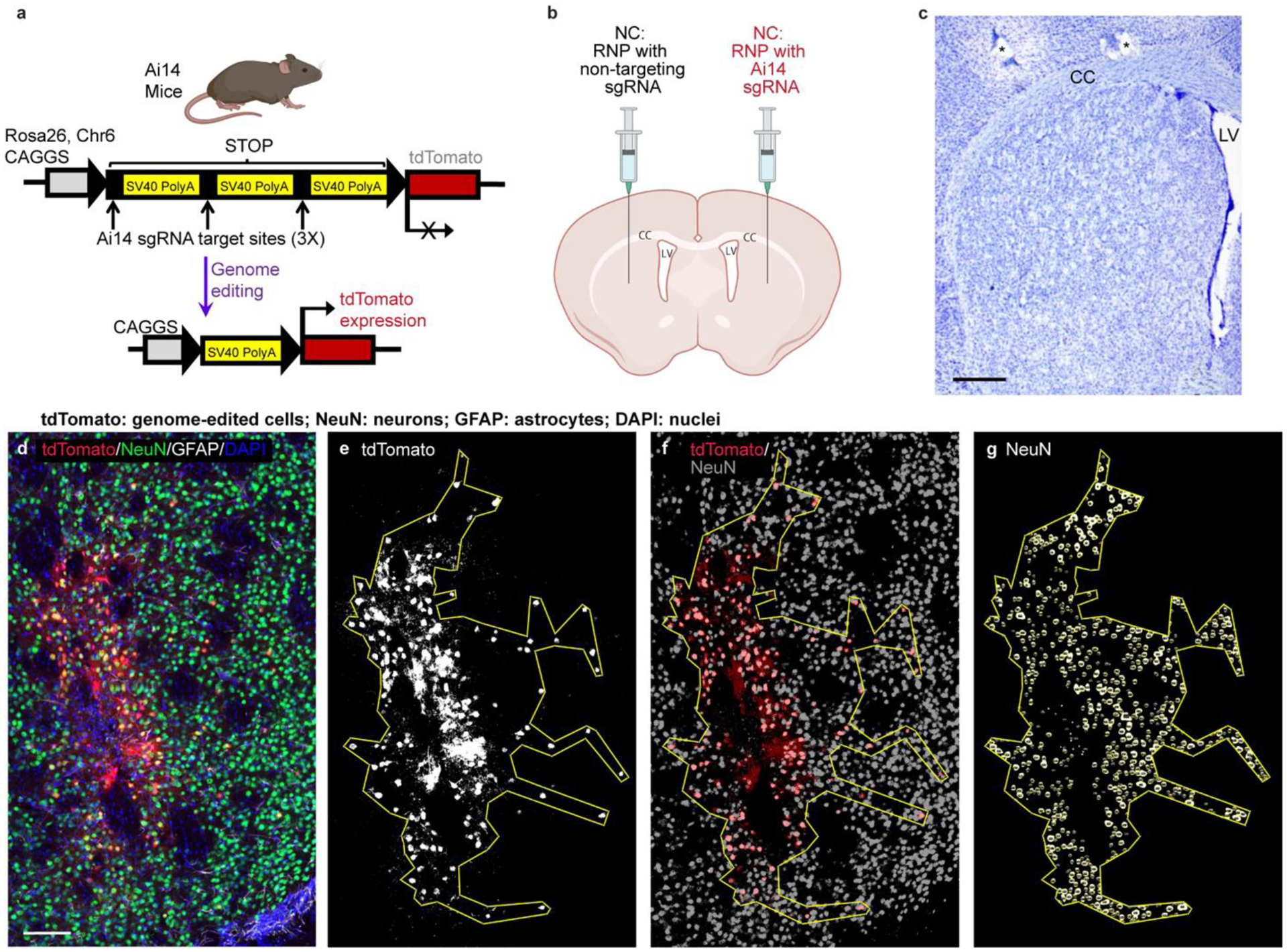
a, Schematic of the Ai14 mouse tdTomato locus. CRISPR/Cas9 targeting sites are present in each of the three SV40 polyA sequences in the STOP cassette. Removal of two of the SV40 polyA cassettes leads to the expression of tdTomato. b, Schematic of the intrastriatal injection of NCs. Created with BioRender.com. CC, corpus callosum. LV, lateral ventricle. c, Nissl-stained coronal mouse section showing normal striatal anatomy. *, holes made during tissue processing to identify left hemisphere. Scale = 500um. d – g, Steps performed for the analysis of edited area size and percent neuronal editing shown in a single representative coronal brain section (animal J4). d, Photomicrograph of genome-edited neurons in the mouse striatum showing maximum intensity projection of three focal planes covering 10 μm. Neurons (NeuN, green) that are genome-edited are tdTomato (red) expressing. GFAP (astrocytes) = white. DAPI (nuclei) = blue. Scale = 100 μm. e, Using FIJI software, a binary mask of the tdTomato channel was used to draw a region of interest (ROI) around the edited, tdTomato+ cells. f, the tdTomato binary mask (red) was then overlayed onto a NeuN signal binary mask (grey) to manually count genome-edited neurons (tdTomato+ and NeuN+). g, Using StarDist2D object identification followed by watershed segmentation of the NeuN signal, the NeuN channel was processed to allow for automated counting of the total number of neurons in the ROI. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; NeuN, neuronal nuclear protein.
