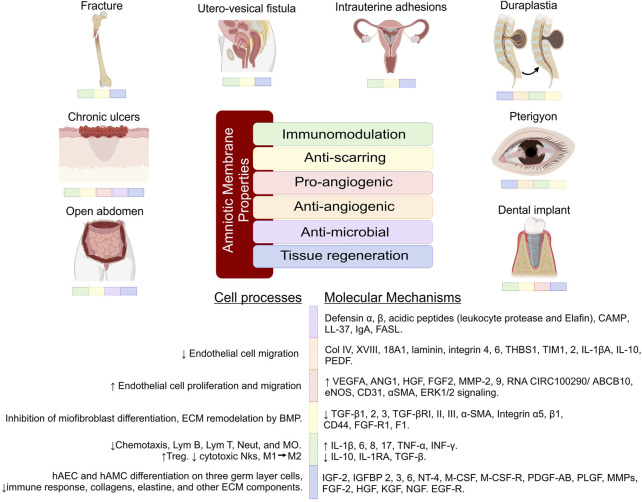
FIGURE 3.
Therapeutic effects of the amniotic membrane and the molecular mechanisms. Each disease has a specific pathophysiology; therefore, the therapeutic effects of AM are different for each of the pathologies. The molecular mechanisms involved are varied, but not all of them are involved in the resolution of the diseases. The figure reinforces the knowledge of the therapeutic effects of AM and also helps to understand future applications of this tissue. Lym, Lymphocyte; MØ, Macrophages; Neut, Neutrophils; MO, Monocytes; Treg, Lymphocyte regulator; NKs, Lymphocytes Natural Killers; CD, Cluster differentiation; αSMA, Smooth muscle actin; ERK, Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Col, Collagen; FGF-R, Fibroblast growth factor receptor; ECM, Extra cellular matrix; MMP, Matrix metalloproteinases; BMP, Bone morphogenetic protein; THBS1, Thrombospondin 1; TIM, T cell immunoglobulin mucin; IL, Interleukin; VEGFA, Vascular endothelial growth factor A; ANG1, Angiopoietin 1; HGF, Hepatocyte Growth Factor; EGF, Epidermal growth factor; FGF, Fibroblast growth factors; eNOS, Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; PDEF, Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor; PDGF, Platelet-derived growth factor; PLGF, Placental Growth Factor; KGF, Keratinocyte growth factor; NGF, Nerve growth factor; TGF, Transforming growth factor; TNF, Tumor necrosis factor; INF, Interferon; IGF, Insulin-like growth factor; IGFBP, Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein; NT, Neurotrophin; M-CSF, Macrophage-colony stimulating factor.