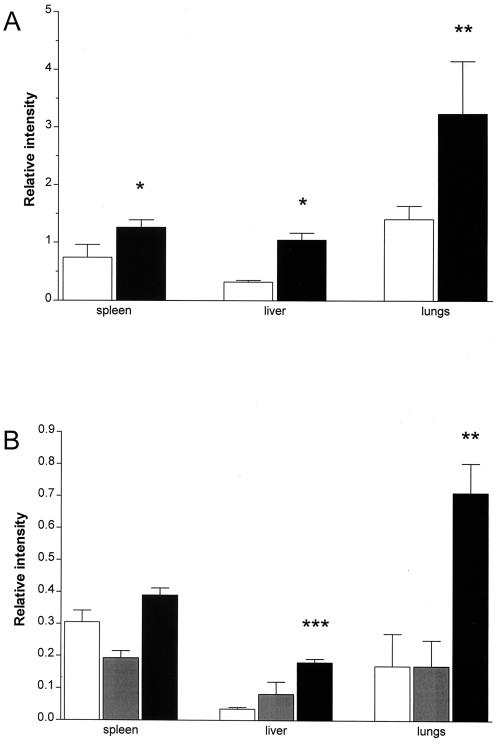
FIG. 8.
Infection with M. tuberculosis induces increased MMP-9 activity in vivo. (A) BALB/c mice were infected i.v. with 106 M. tuberculosis H37Rv bacteria, and homogenates were prepared from spleens, livers, and lungs of sham-infected age-matched controls (white bars) and of infected mice (black bars) 5 months later and analyzed by gelatin zymography. (B) SCID mice were infected i.v. with 106 M. tuberculosis H37Rv bacteria, and homogenates were prepared from spleens, livers, and lungs of sham-infected age-matched controls (white bars) and of infected mice 8 days (grey bars) and 22 days (black bars) later and analyzed by gelatin zymography. Data are presented as means + standard deviations of the relative enzymatic activity in samples from individual mice (three per group) with the same total protein content loaded (lungs, 20 μg; spleens, 3 μg; and liver, 40 μg of total protein/lane). ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001 when comparing with the uninfected animals.