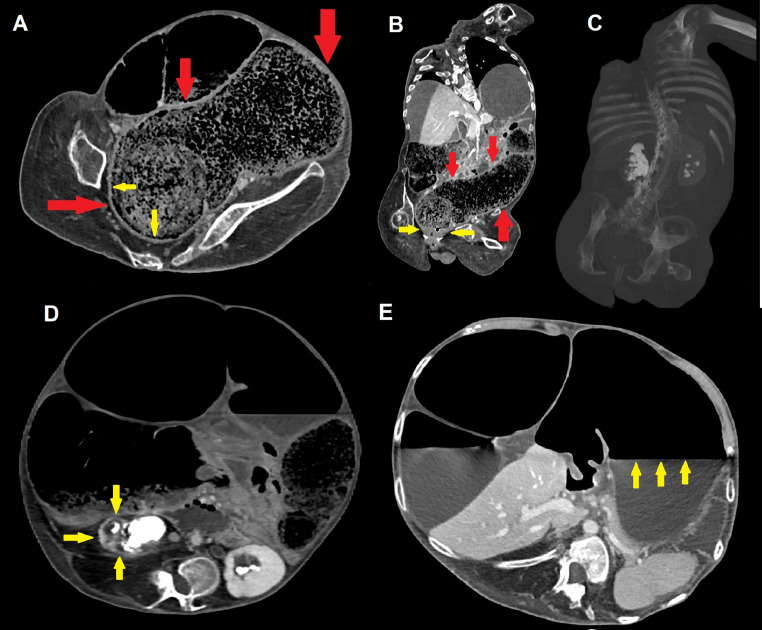
Fig. 3.
Contrast-enhanced CT scans on a lower level (A) and coronal view on MPR (B) demonstrate an extensive recto-sigmoid fecaloma (measuring more than 30 × 10 cm; red arrows); chronic thickening of rectal walls is visible (yellow arrows), as well as compressive bilateral I-grade hydronephrosis, renal stones and thinning of renal parenchyma (frequent in DMD; C and D [yellow arrows]). Dilatation with atonia and an evident fluid-air level also involves the stomach (E [yellow arrows]), further witnessing the multifocal nature of GI motility disturbances in patients with DMD.