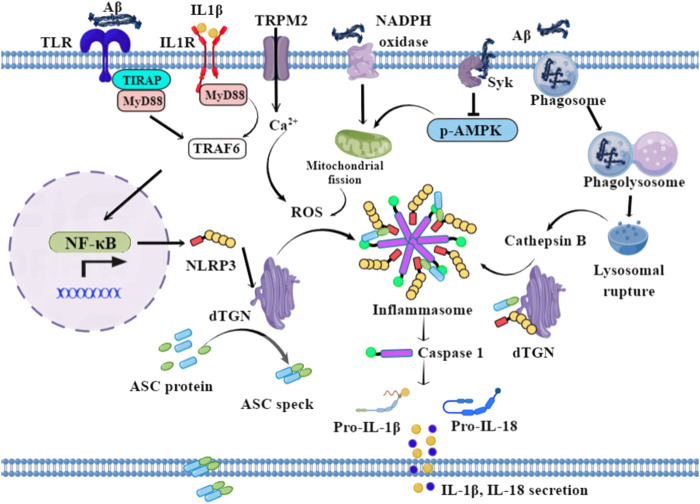
FIGURE 1.
Possible mechanisms of NLRP3 activation in microglia. In the initiation signal, Aβ fibrils bind to TLR, and drive the transcription of NLRP3, pro-IL-1β, and pro-IL-18 via NF-κB signaling. In the activating signal, the lysosomal-rupture pathway and ROS generation pathway are the two classical routes for NLRP3-mediated caspase-1 activation. The phagocytosis of aggregated Aβ by microglia triggers lysosomal rupture and the subsequent release of cathepsin B into the cytosol. In addition, Aβ triggers Ca2+ influx via TRPM2 and activates NADPH oxidase and Syk, subsequently inducing mitochondrial fragmentation and the generation of ROS. Therefore, the stimuli—including ROS and cathepsin B—drive the dispersed transGolgi network (dTGN) to recruit NLRP3 through ionic bonding, leading to adaptor protein ASC polymerization and downstream signaling activation.