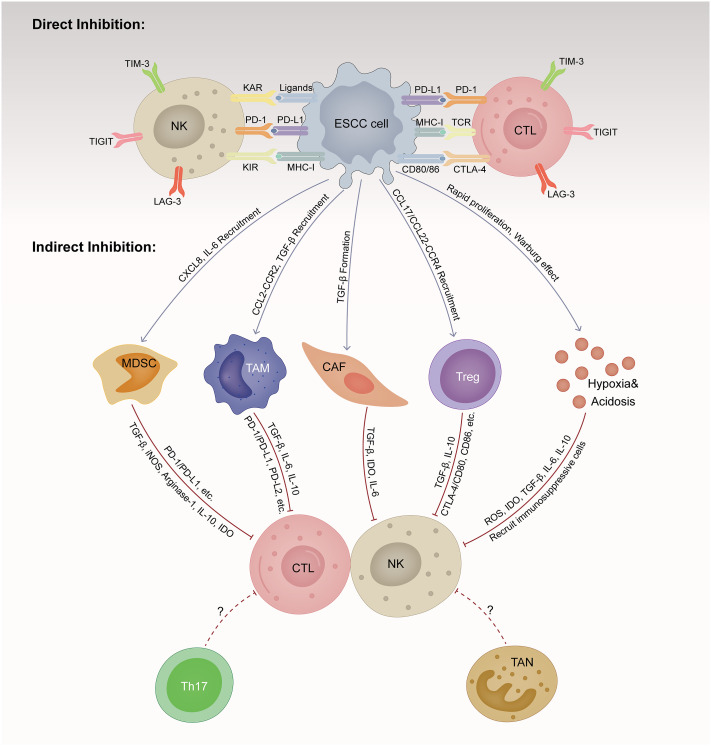
Figure 1.
Immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) in esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC). TME is a dynamic complex and comprehensive system, composed of various cellular components and non-cellular components. ESCC cells are born to create an immunosuppressive milieu suppressing the proliferation and function of cytolytic NK and T cells directly and indirectly. ESCC, esophageal squamous cell cancer; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; NK, natural killer cell; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; Treg, regulator T cell; TAN, tumor-associated neutrophils; Th17, T helper cell 17; MHC-1, major histocompatibility class I; TCR, T cell receptor; KAR, killer activation receptor; KIR, killer inhibitory receptor; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; PD-L2, programmed cell death ligand 2; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; LAG-3, lymphocyte activation gene-3; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein-3; TIGIT, T-cell immunoglobulin and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif domain; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; IL, interleukin; CXCL, CXC motif chemokine ligand; CCL, CC motif chemokine ligand; CCR, CC motif chemokine receptor; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase-2; ROS, reactive oxygen species.