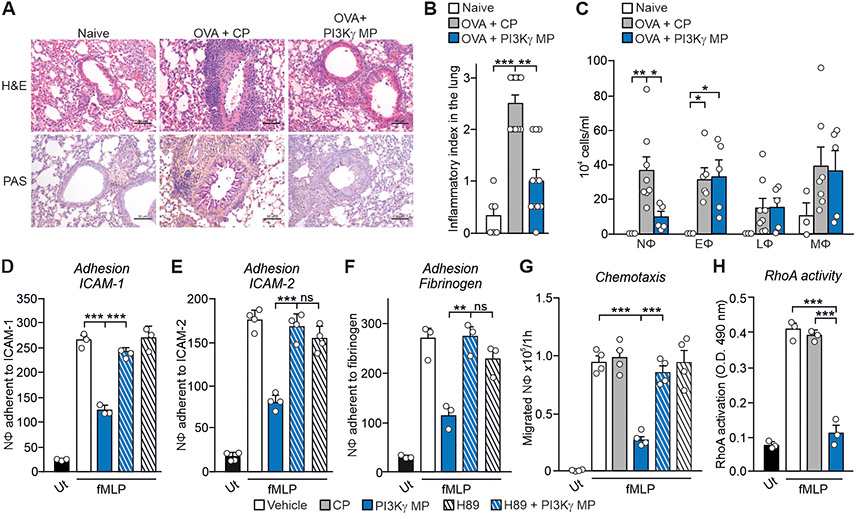
Fig. 5. PI3Kγ MP limits neutrophilic lung inflammation in asthmatic mice.
(A) Representative images of hematoxylin-eosin (top) and periodic acid-Schiff’s reagent (bottom) staining of lung sections of naïve and ovalbumin (OVA)-sensitized mice, pre-treated with PI3Kγ MP (25 μg) or CP (equimolar amount), before each intranasal OVA administration (days 14, 25, 26 and 27 of the OVA sensitization protocol). Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Semi-quantitative analysis of peribronchial inflammation in lung sections as shown in (A). Naïve n=6, OVA+CP n=8 and OVA+PI3Kγ MP n=5 mice. (C) Number of neutrophils (NΦ), eosinophils (EΦ), lymphocytes (LΦ) and macrophages (MΦ) in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid of mice treated as in (A). Naïve n=3, OVA+CP n=8 and OVA+PI3Kγ MP n=5 animals. (D to F) fMLP-induced adhesion to ICAM-1 (D), ICAM-2 (E) and fibrinogen (F) of human neutrophils pre-treated or not with the PKA inhibitor H89 (200 nM, 30 min) before exposure to vehicle or PI3Kγ MP (50 μM, 1 hour). Static adhesion was induced with 25 nM fMLP for 1 min. Average numbers of adherent cells/0.2 mm2 is shown. In (D) and (F), n=3 in all groups; in (E), n=4 in all groups. (G) fMLP-triggered chemotaxis of human neutrophils treated with vehicle, CP (50 μM) or PI3Kγ MP (50 μM) for 1 hour, without or with pre-treatment with the PKA inhibitor H89 (200 nM, 30 min). n=4 in all groups. (G) fMLP-induced RhoA activity in human neutrophils treated with vehicle, CP (50 μM) or PI3Kγ MP (50 μM). n=3 in all groups. In (B), **P<0.01 and ***P <0.001 by Kruskal Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test. In (C), (D), (E), (F), (G) and (H), *P <0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P <0.001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test.