Figure 6. Associations of inflammation and permeability markers with infant fecal metagenomes and metabolomes.
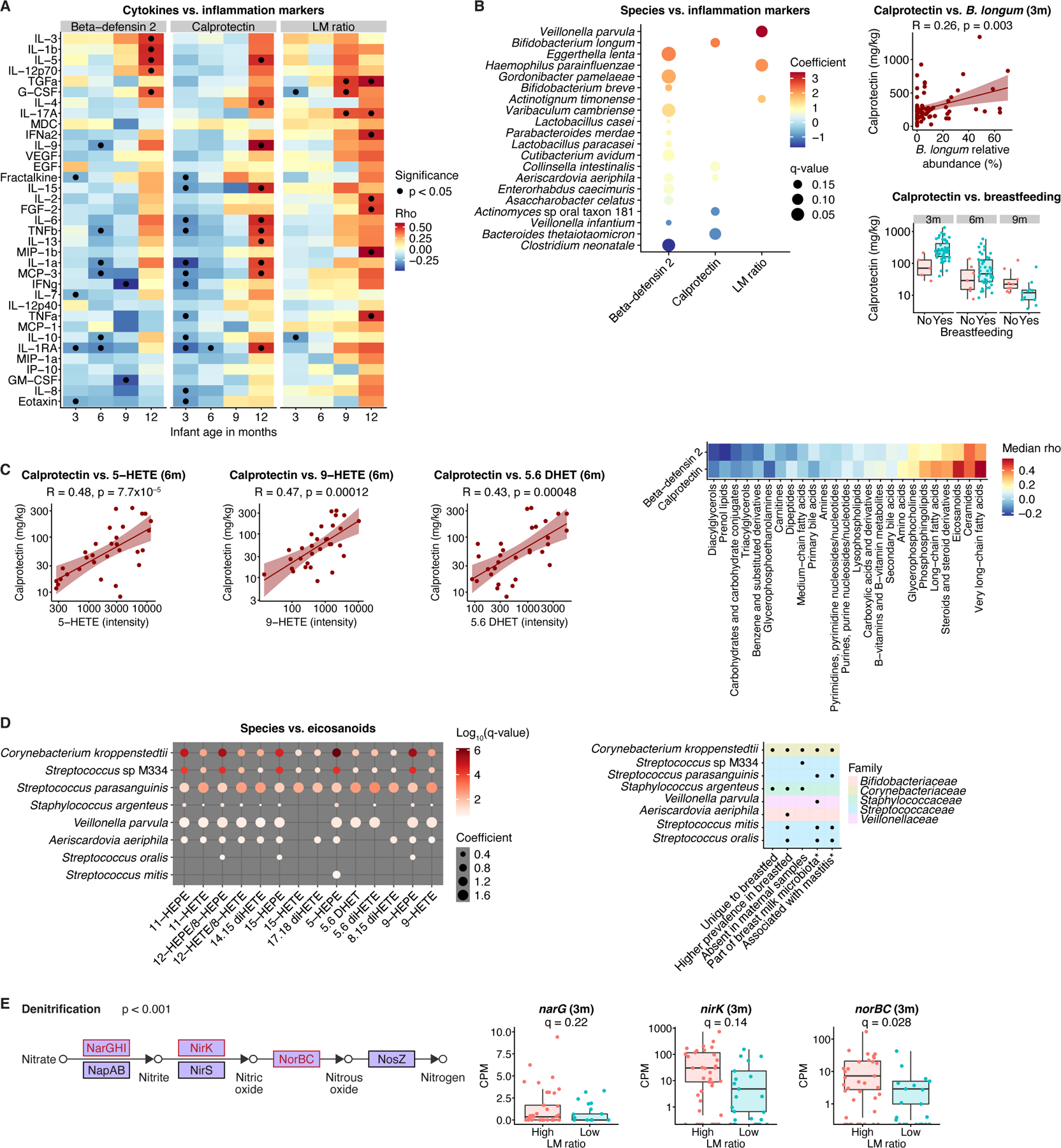
A) Markers of intestinal permeability and inflammation were inversely correlated with proinflammatory serum cytokines during the first months of life but positively correlated at one year of age. B) Left panel: Calprotectin and beta-defensin 2 were positively associated with beneficial species in infants up to 6 months old. Effects are from general linear models, corrected for longitudinal sampling, age, sex, delivery mode, antibiotics, breastfeeding, and formula use/type. Right panels: Calprotectin levels were higher in breastfed infants and correlated with Bifidobacterium longum relative abundance. C) Calprotectin levels were positively correlated with fecal eicosanoids, particularly arachidonic acid metabolites in 6-month-old infants. R values for scatter plots in (B, C) are Kendall’s tau. D) Levels of infant fecal eicosanoid metabolites were positively associated with relative abundances of species previously linked to the breast milk microbiome, including causative agents of mastitis. *based on previous literature21,22,55. Results (left) are from general linear models, corrected for longitudinal sampling, age, sex, delivery mode, antibiotics, and formula use/type. E) LM ratio was positively associated with microbial genes linked to denitrification via nitric oxide production. The cut-off of 0.03 for high versus low LM ratio was determined a priori. Overall p-value for denitrification enrichment was obtained by Fisher’s exact test. q-values derived from a general linear model including infants aged up to one year, corrected for longitudinal sampling, age, sex, delivery mode, antibiotics, breastfeeding, and formula use/type. For boxplots, midlines represent the median, boxes the interquartile range (25th to 75th percentile), and whiskers the range of data. See also Figure S6; Table S1.
