Figure 7. The CD19-CAR+CD38-CCR combination elicits improved in vivo anti-tumor function against tumor variants with very low antigen density.
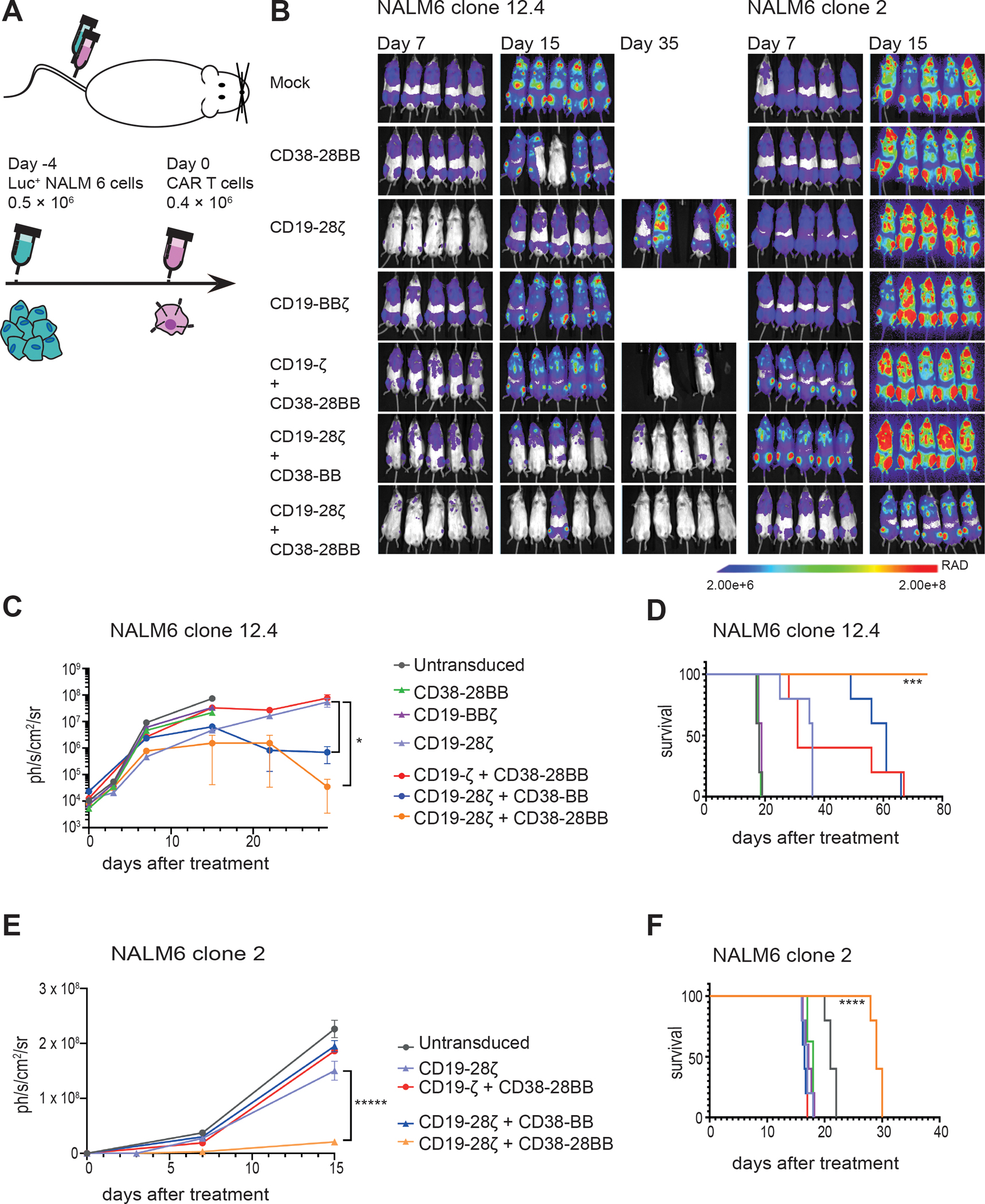
(A) A schematic representation of the ALL in vivo model is shown. 0.5 × 106 FFLuc-GFP NALM6 clone 12.4 or NALM6 clone 2 cells were administrated intravenously. Untransduced, CD38-28BB, CD19-ΒΒζ, CD19-28ζ, CD19-ζ+CD38-28BB, CD19-28ζ+CD38-BB or CD19-28ζ+CD38-28BB CAR T cells were infused intravenously 4 days later. Tumor burden was measured weekly by BLI. (B) Representative images of three time points are shown with the pixel intensity represented in color. (C) Average tumor burden of mice injected with FFLuc-GFP NALM6 clone 12.4 cells is shown over time. Tumor burden is depicted as units of photons per second per square centimeter per steradian (ph/sec/cm2/sr) (n=5 mice per group). (D) Survival of mice injected with NALM6 clone 12-4 is shown. (E) Average tumor burden of mice injected with FFLuc-GFP NALM6 clone 2 cells is shown over time. Tumor burden is depicted as units of photons per second per square centimeter per steradian (ph/sec/cm2/sr); n=5 mice per group. (F) Survival of mice injected with NALM6 clone 2 is shown. Statistical analysis of tumor burden (C and E) was performed with two-way ANOVAs and subsequent multiple comparison, corrected by Turkey test. *p<0.05. Statistical analysis of survival (D and F) was performed with log-rank tests. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
