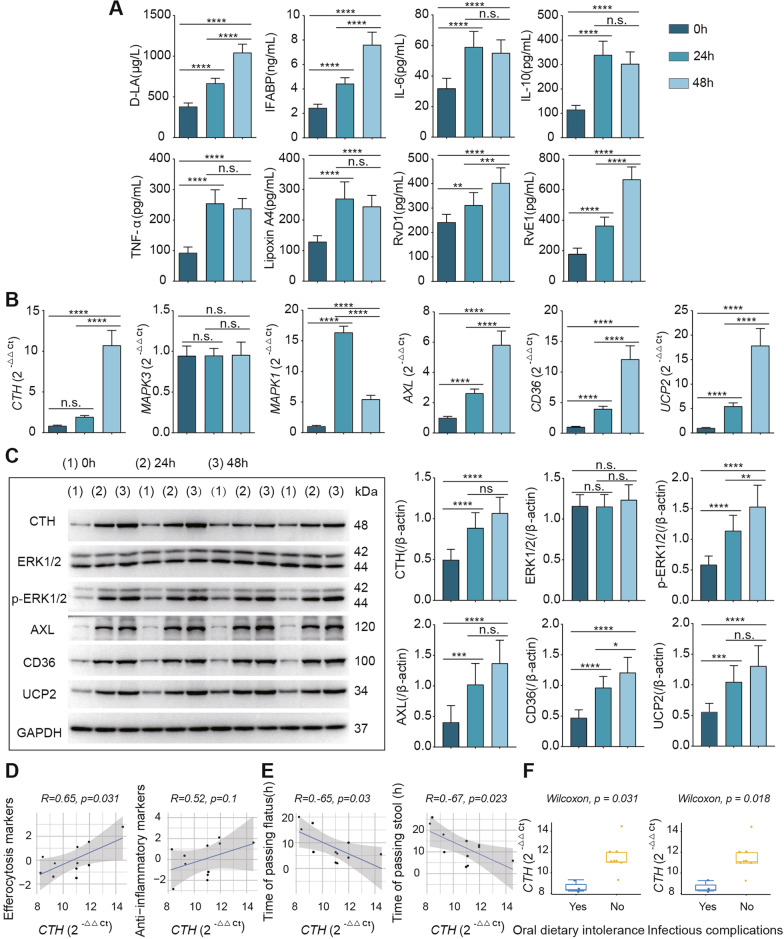
Fig. 8.
Clinical validation of changes in Cth, ERK1/2 and efferocytosis levels with the recovery of intestinal function and correlation analysis. A Postoperatively, the levels of intestinal barrier indicators (D-LA, IFABP), inflammatory factors (IL-6, TNF-α), anti-inflammatory factors (IL-10) and repair indicators (Lipoxin A4, RvD1, RvE1) changed as intestinal function was restored. B, C Postoperatively, changes in the gene levels of Cth, ERK1/2 and efferocytosis molecules (AXL, CD36, UCP2) were observed with prolonged intestinal recovery time. D Cth showed a positive correlation with efferocytosis biomarkers (AXL, CD36, UCP2) and anti-inflammatory repair indicators (IL-10, Lipoxin A4, RvD1, RvE1). E Correlation analysis of the mRNA levels of Cth at 48 h after surgery with the time of passing flatus and stool, suggesting that higher Cth levels were associated with less time for bowel function to resume. F Cth levels in patients with and without oral dietary intolerance at 48 h after surgery and in patients with and without infectious complications at 7 days after surgery. 0 h: the time of surgery; 24 h: 24 h after surgery; 48 h: 48 h after surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The Wilcoxon rank sum test (two-group comparisons) or Pearson correlation (correlation tests) was used accordingly, and statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05