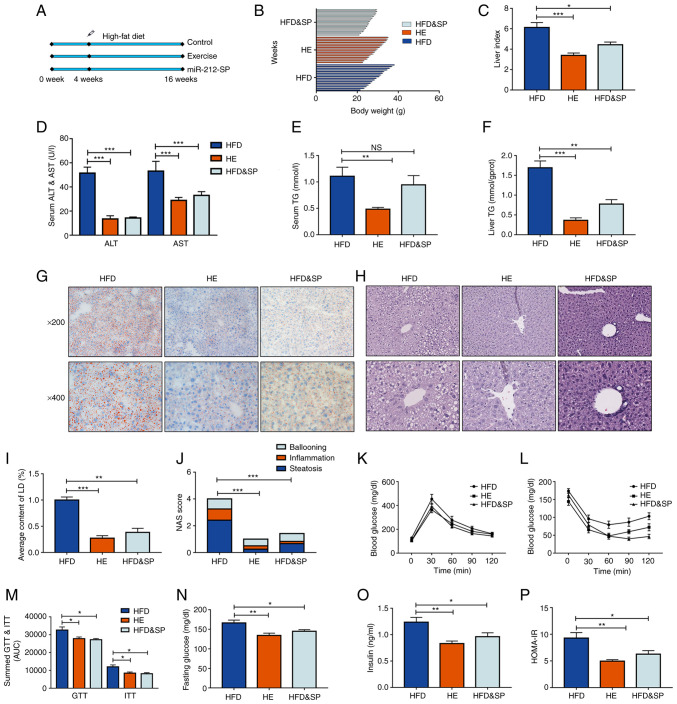
Figure 3.
Inhibition of miR-212-3p expression mimics the effects of exercise to improve lipid accumulation induced by a HFD. (A) The experimental protocol for the animals. (B-D) The body weight, liver index, and serum ALT and AST levels were increased in the HFD group, while they were decreased in the HFD and SP, and HE group. (E and F) The liver TG content and serum TG content exhibited a similar decrease following the inhibition of miR-212-3p compared with exercise treatment. (G-J) Hematoxylin and eosin and Oil Red O staining confirmed the ameliorative effect of miR-212-3p inhibition on lipid accumulation. (K-M) Similar to exercise treatment, the inhibition of miR-212-3p improved glucose homeostasis through GTT and ITT. (N-P) Similar to exercise therapy, the inhibition of miR-212-3p improved insulin resistance through fasting blood glucose, serum insulin and the calculated HOMA-IR. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. NS, not significant; HFD, high-fat diet; ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase; SP, serotype (mice that received the tail vein injection of recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 8 gene vectors); TG, triglyceride; LD, lipid droplets; NAS, NAFLD activity score; GTT, glucose tolerance test; ITT, insulin tolerance test; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HE, high-fat diet and exercise.