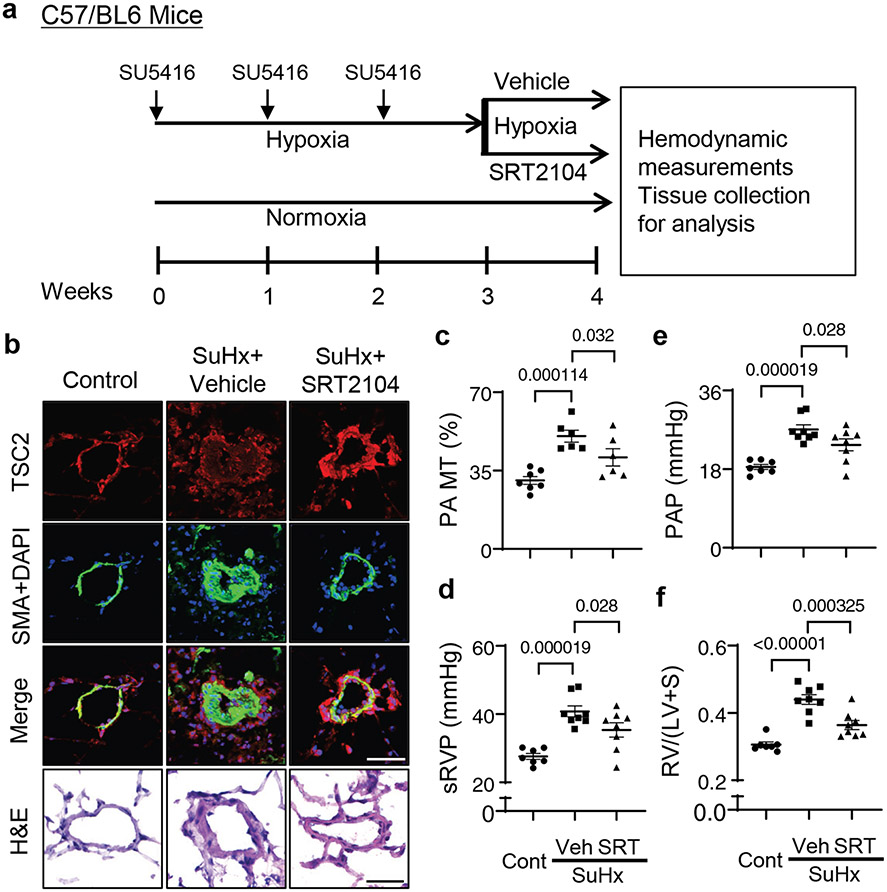
Figure 6. SRT2104 restores TSC2 in small PAs, attenuates PH, and reduces RV hypertrophy in mice.
a. Six to eight week old male and female mice were maintained under hypoxia for three weeks and received SU5416 injection at the beginning of every week. Starting at week 4, mice kept under hypoxia were randomly assigned to receive SRT2104 (SRT) or vehicle (Veh) for 5 days/week for one week, and hemodynamic and morphological analyses were performed. Controls were same-age and -sex mice kept under normoxia.
b. Immunohistochemical analysis to detect TSC2 (red), SMA (green), and DAPI (blue). Images are representative of 3 mice/group, 12 PAs/mice. Scale bar, 80 μm. For H&E staining, images are representative from 7 control mice and 6 SuHx+Vehicle or SuHx+SRT2104, 12 Pas/mouse. Scale bar, 30μm,
c. PA medial thickness (PA MT) was calculated from 12-24 Pas/mouse. Data are means±SE from n=7 control mice (3 male, 4 female), n=6 PH mice (3 male, 3 female), n=6 PH+SRT2104 mice (3 male, 3 female) groups. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with a Fisher’s LSD post hoc test.
d-f. Systolic right ventricular pressure (sRVP) (d), pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP) (e), and Fulton index (RV/(LV + septum) weight ratio) (f) were calculated. Data are means±SE from n=7 control mice (3 male, 4 female), n=8 PH mice (4 male, 4 female), n=8 PH+SRT2104 mice (4 male, 4 female) groups. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with a Fisher’s LSD post hoc test.