Fig. 1.
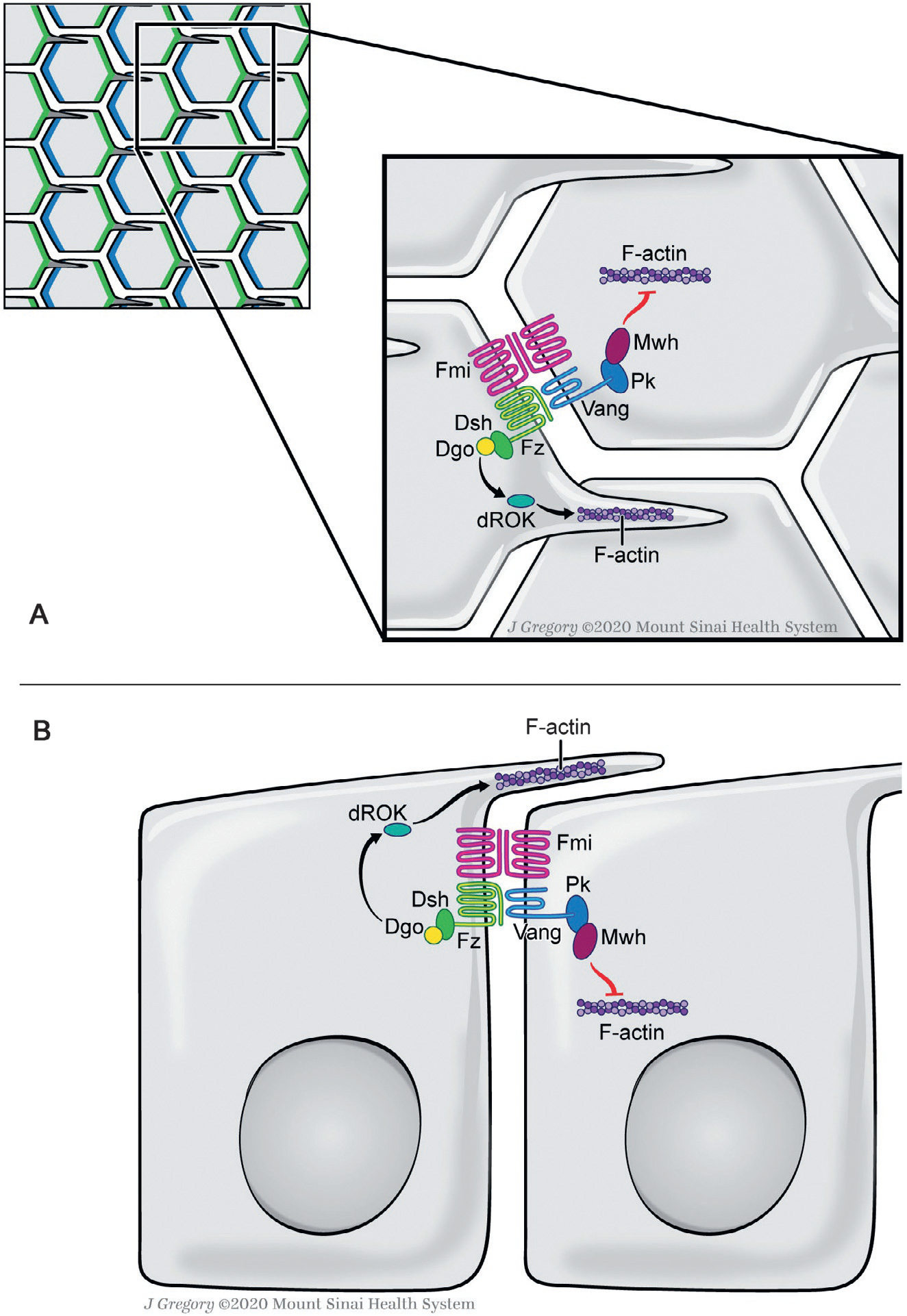
Planar cell polarity in the Drosophila wing epithelium. Schematic X-Y (top) view in (A) and lateral (Z-section) view in (B) of core PCP complexes is shown. Note that the core PCP complexes are located at/near the adherens junctions in the subapical domain of the cells. In wing epithelia, one of the simplest PCP paradigms, asymmetric distribution of the core PCP factors starts to emerge at late larval stages and is most obvious in pupal stages (shown in upper left panel schematic, Fz-Dsh-Dgo (blue) and Vang-Pk complexes (green), both stabilized by interactions with Fmi, asymmetrically localize in distal and proximal apical membranes, respectively (Adler, 2012; Goodrich & Strutt, 2011; Humphries & Mlodzik, 2018; Jenny, 2010; Peng & Axelrod, 2012; Seifert & Mlodzik, 2007; Wu & Mlodzik, 2009). The PCP complexes then trigger the polarization of the cytoskeleton through downstream regulators to ensure single spike actin hair formation via the Fz/Dsh/Dgo complex at the distal vertex of each cell (Gault, Olguin, Weber, & Mlodzik, 2012; Strutt & Warrington, 2008; Winter et al., 2001; Yan et al., 2008). Proximal is left. See main text for further details.
