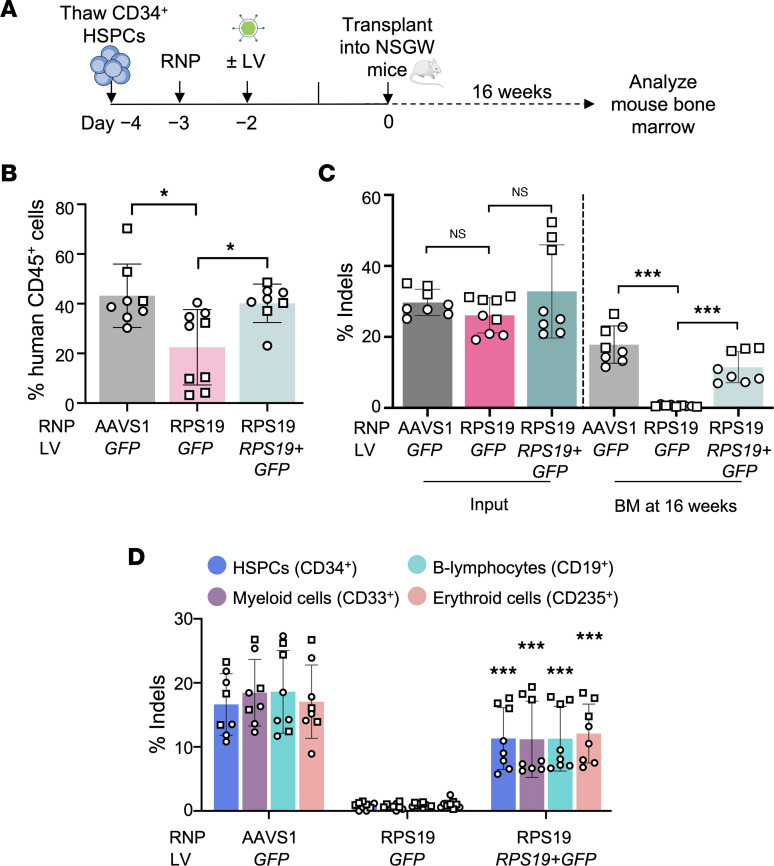
Figure 5. RPS19+/– HSPCs exhibit defective bone marrow repopulation after xenotransplantation.
(A) Experimental scheme for xenotransplantation studies. CD34+ HSPCs (n = 2 different donors) were edited with the indicated RNPs followed by transduction with LVs encoding GFP or RPS19 plus GFP at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 20. A total of 4 × 105 to 5 × 105 live cells were transplanted into NSGW mice (n = 8–9 mice), which were euthanized and analyzed after 16–18 weeks. (B) Percentage of human CD45+ cells in recipient bone marrow. Data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA test and pairwise testing was performed with Tukey’s adjustment for multiple comparisons. (C) Indel frequency in input donor CD34+ HSPCs on day 0 and in donor-derived cells in recipient mouse bone marrow at 16–18 weeks after xenotransplantation. Data were analyzed by Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test. (D) Indel frequencies in CD34+ HSPC donor-derived hematopoietic lineages purified from recipient mouse bone marrow by flow cytometry using the indicated antibodies. The frequency of human T cells in recipient bone marrow was <0.01% (not shown). Data were analyzed by unpaired, 2-tailed Student’s t test. Asterisks indicate significant differences between RPS19-edited HSPCs transduced with RPS19 plus GFP LV versus GFP LV. All charts show the mean ± SD, with each dot representing an individual mouse and each symbol representing a different CD34+ cell donor. P values were adjusted for multiple comparison by the Holm-Bonferroni method unless specified otherwise. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.