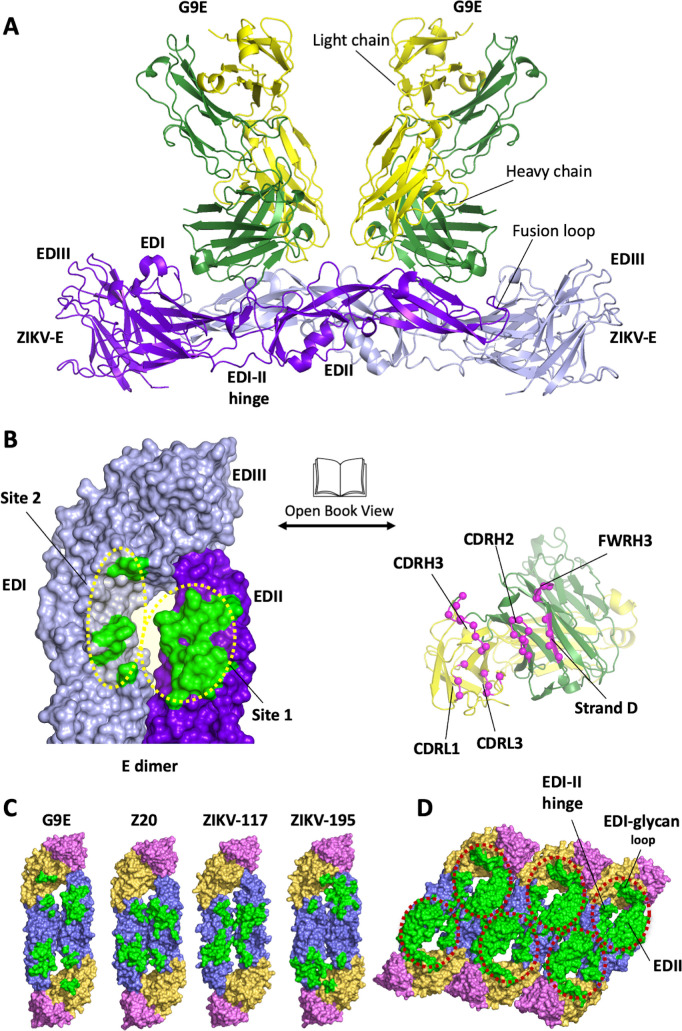
Fig 1. G9E targets an immunodominant quaternary epitope on ZIKV E-protein.
(A) Structure of ZIKV E in complex with G9E. The structure reveals that two G9E Fab fragments bind the E-dimer in a similar mode. G9E Fab fragments and E-dimer are shown in cartoon representation (green—Fab heavy chain; gold—Fab light chain; ZIKV E dimer (protomer 1—purple; protomer 2—lavender). (B) G9E binds a quaternary epitope formed on E-dimer. Open book representation of the interface formed between E-dimer (green) and G9E (pink) are shown. The quaternary epitope comprises a major (site 1) and a minor (site 2) site on E-dimer. The paratope comprises heavy and light chain CDRs. (C) G9E targets an immunodominant epitope centered on EDII. G9E footprint on ZIKV E-dimer overlaps with previously described neutralizing human mAbs ZIKV-117, Z20, and ZIKV-195 isolated from patients infected with ZIKV. The quaternary epitopes targeted by the respective neutralizing mAbs are shown in green. E domains are shown in orange (EDI), blue (EDII) and pink (EDIII). ZIKV-195 epitope was obtained from ZIKV/ZIKV-195 structure (PDB ID: 6MID). ZIKV-117 footprint was derived from the mAb (ZV-67) fitted in the Cryo-EM map of ZIKV/ZIKV-117 structure (PDB ID: 5UHY). ZV20 epitope was obtained from ZIKV/Z20 structure (PDB ID: 5GZO). (D) Combined EDII targeting antibody epitope defines an immunodominant region on ZIKV E-raft. Combined epitope comprised of G9E, Z20, ZIKV-117, and ZIKV-195 is shown within the red circle, including EDII, EDI-II hinge, and the EDI glycan loop.