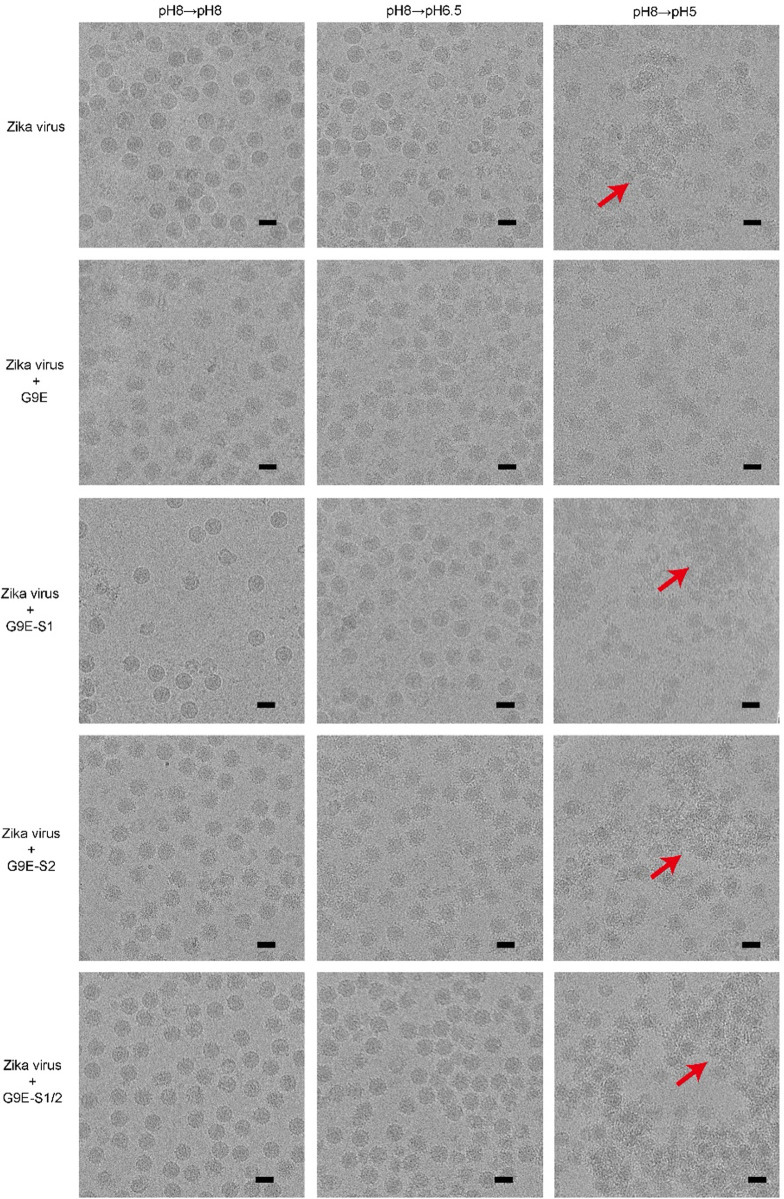
Fig 6. Cryo-EM micrographs of the G9E Fab and its mutants complexed with Zika virus under various pH conditions: pH 8.0→pH 8.0 and pH 8.0→pH 6.5, and pH 8.0→pH 5.0.
In the uncomplexed ZIKV control, virus particles are largely smooth surfaced at pH 8.0. At pH 8.0→pH 5.0, the virus particles have a disordered surface and have aggregated (red arrow). When ZIKV is complexed with G9E Fab, the virus particles under all pH conditions appear spiky, indicating Fab binding. At pH 8.0→pH 5.0, no aggregation is detected, which suggests G9E Fab can inhibit virus-virus fusion. When ZIKV is mixed with Fab G9E-S1, at pH 8.0→pH 8.0, virus particles remain smooth surfaced, similar to that in the uncomplexed ZIKV control, indicating Fab G9E-S1 could not bind to ZIKV. When ZIKV is complexed with either G9E-S2 or G9E-S1/2, at pH 8.0→pH 8.0 and pH 8.0→pH 6.5, the particles appear spiky, indicating that Fabs bind them. At pH 8.0→pH 5.0, aggregation is observed (red arrow), suggesting that these Fabs cannot inhibit virus-virus fusion. Scale bars, 500 Å.