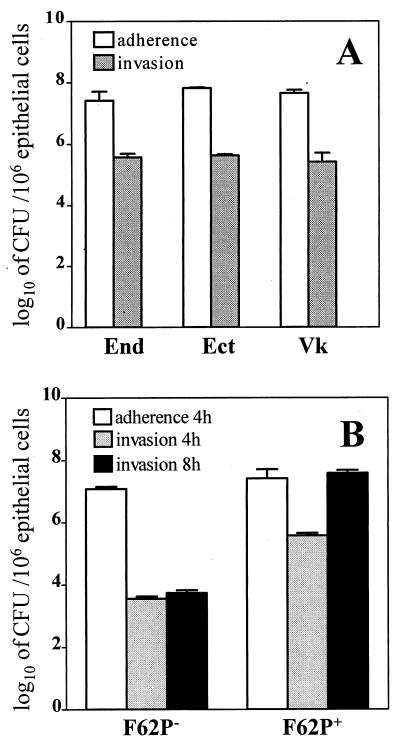
FIG. 1.
Interactions of N. gonorrhoeae with human cervical and vaginal epithelial cells. (A) Adherence of the N. gonorrhoeae F62 piliated variant to and invasion of the endocervical (End), ectocervical (Ect), and vaginal (Vk) immortalized epithelial cell lines 4 h postinfection. (B) Adherence and invasion of nonpiliated (F62P−) and piliated (F62P+) N. gonorrhoeae F62 following 4 and 8 h infection of endocervical epithelial cells. Values are means plus standard deviations of logarithmically transformed determinations obtained from three independent experiments.