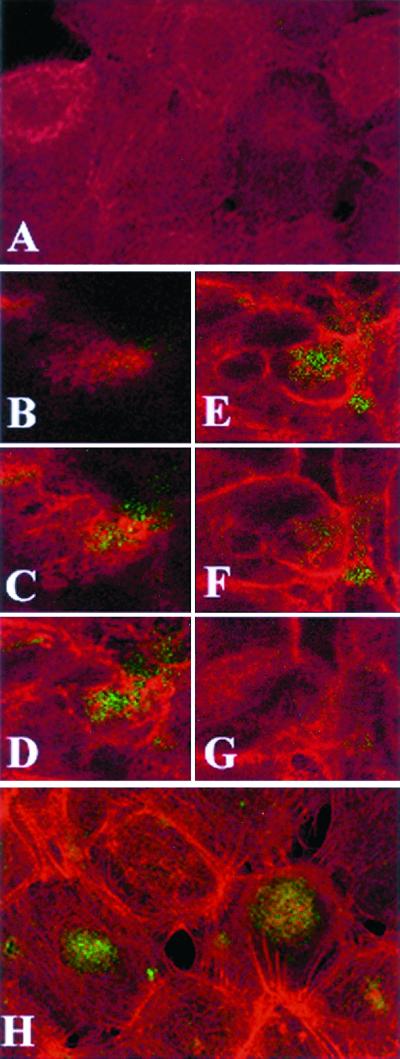
FIG. 2.
Confocal microscopy analysis of endocervical epithelial cell monolayers infected with GFP-expressing N. gonorrhoeae. F actin was visualized using red fluorescent Alexa-Fluor. Images were obtained by combining a Z series of 15 optical sections taken at 2-μm intervals. The slides were consecutively read for red and green fluorescence using 485- and 568-nm filters, respectively. (A) Control uninfected culture. Diffuse red staining indicates lack of F-actin polymerization. (B to G) Single apical-basal confocal slices taken in consecutive order (1, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 optical sections) from a Z series 30 min postinfection. The Alexa-Fluor labeling (C to G) demonstrates increased cortical polymerization of F actin in most epithelial cells. The GFP Alexa-Fluor overlap (yellow color [C to F]) indicates colocalization of F actin with gonococci. (H) Composite image of a 15-section Z series 4 h postinfection. GFP-expressing gonococci appear in large round clusters within the infected epithelial cells (typically seen between the sixth and tenth optical sections). Polymerized actin bundles extend toward the middle of infected epithelial cells.