Figure 3. KAT6 catalytic domain substrate interactions and drug bound state.
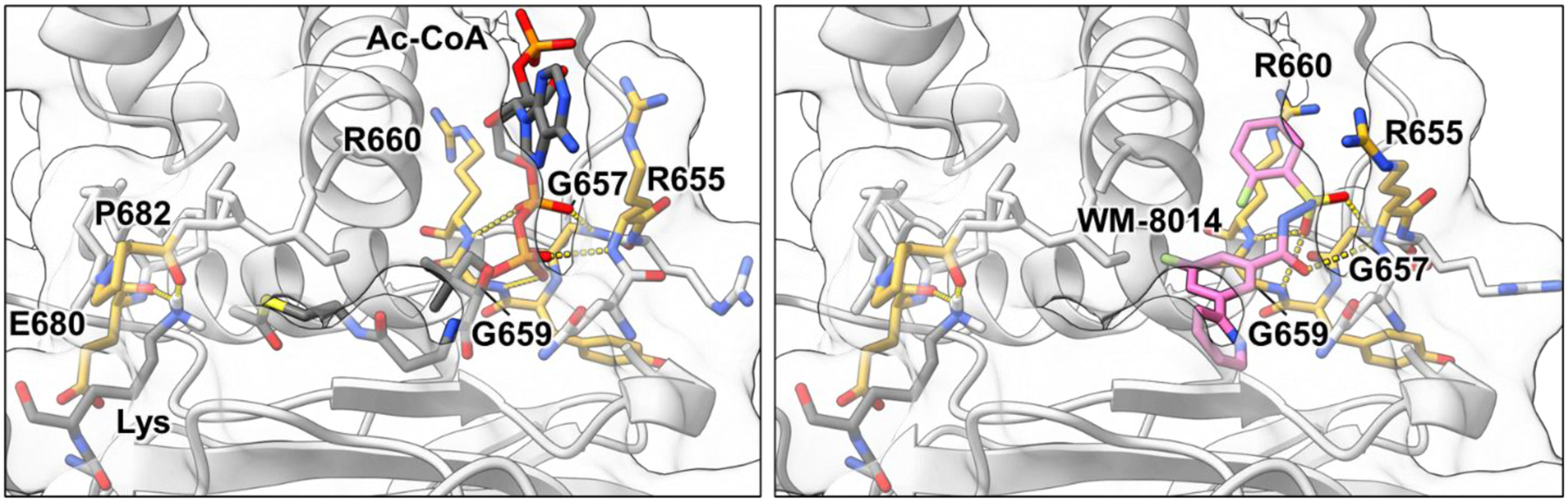
Left. Catalytic interactions of the MYST1 HAT domain (white) including hydrogen bonding between the phosphodiester and phosphate of CoA and the backbone amides of Arg655, Gly657, Gly659 and R660 (yellow). Hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl of Glu680 Pro682 (yellow) direct the substrate lysine Nε (PDBID 6BA4, 6VO5).9, 56 Composite substrate-bound structure was energy minimized using Rosetta 3.13 fast relax.50 Right. Occupancy of the acetyl-CoA binding site by competitive ligand WM-8014 (pink) including hydrogen bonding interactions between the acylsulfonylhydrazide core and the backbone amides of Arg655, Gly657, Gly659 and R660 (yellow). This binding is anchored by additional hydrophobic interactions that are not depicted here (PDBID 6CT2).9
