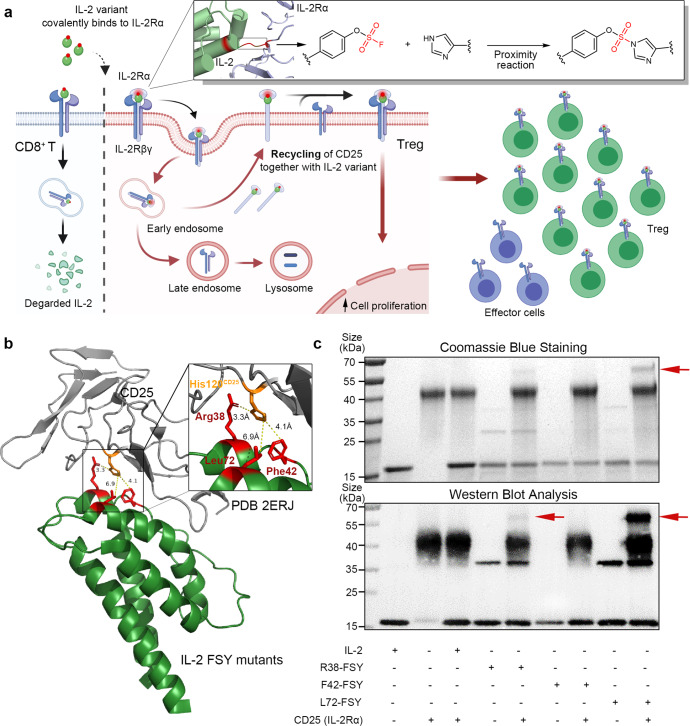
Fig. 1.
Genetic code expansion-mediated incorporation of FSY to generate an IL-2 variant that covalently binds to IL-2Rα. a Schematic representation of the selective covalent binding-mediated augmentation of the recycling and extracellular maintenance of IL-2 on Tregs. Upon the binding of IL-2 to its high-affinity trimeric IL-2 receptor expressed on Tregs, the quaternary IL-2−receptor complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent dissociation in the early endosome. IL-2Rα can then be recycled back to the cell surface, whereas IL-2 associated with other subunits undergoes degradation in the lysosome. The incorporation of FSY into IL-2 allows it to covalently bind to IL-2α with infinite affinity, thereby distinctly augmenting the recycling of IL-2 and promoting IL-2 signalling sustainably preferentially on Tregs. b Crystal structure of human IL-2 assembled together with IL-2α (PDB number: 2ERJ) showing selected sites in stick form. All sites were within 10 Å of the selected H120 site of IL-2Rα. c Analysis of the covalent binding of FSY-bearing IL-2 variants to IL-2α. Equal doses of purified WT-IL-2 and IL-2 variants were incubated with the His-tagged ectodomain of IL-2Rα (IL-2Rα-His) at room temperature overnight, and the denatured samples were then analysed by Coomassie blue and western blotting (WB). The anti-His antibody was used as the primary WB antibody. The red arrows indicate the covalent crosslinking of IL-2 and IL-2Rα. See also Supplementary Fig. 2