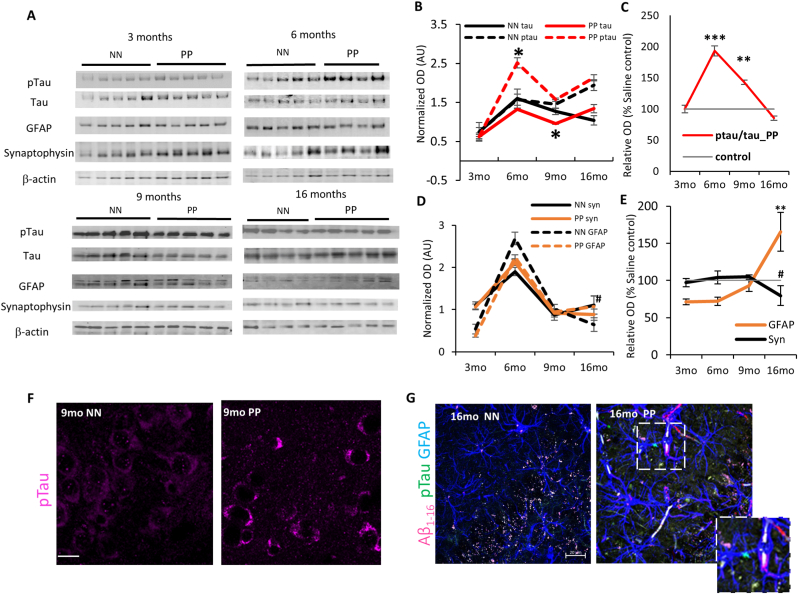
Fig. 2.
The Effect of PolyI:C on p-tau accumulation in the hippocampus: (A) Immunoblots of hippocampal lysate from PP and NN mice at 3, 6, 9 and 16 months, for p-tau, tau, GFAP, Synaptophysin. β-Actin was used as housekeeping control. (B,D) Relative quantification of Tau, GFAP and Synaptophysin represented in normalized optical density. (C,E) Percentage of relative changes of these proteins compared to the saline treated controls. Representative immunostaining for (F) p-tau (9 months) and (G) p-tau, Aβ1-16 and GFAP at 16 months age group. Insert shows a GFAP positive process with internalized p-tau aggregates. Scale bar in F is 45 μm, G is 20 μm. Values represented as mean ± SEM, n = 4–5 mice per age and treatment. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005 #p = 0.07. Statistical significance based on two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc analysis.