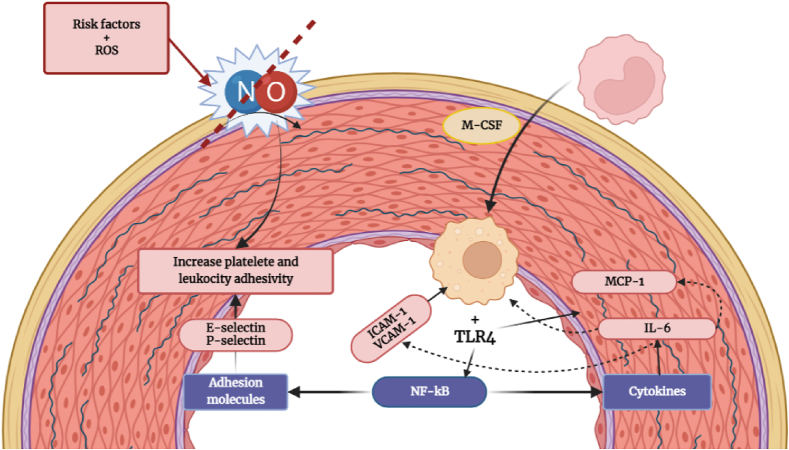
Fig. 1.
The decrease of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis increases leukocytes and platelets adhesivity. Macrophages uptake oxidized LDL (oxLDL), finally triggering inflammation. OxLDL binds to TLR4 which promote the release of interleukine (IL-6) and monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP-1) among others. As a cycle MCP-1 let monocytes to migrate and infiltrate into subendothelial space differentiating into macrophages by the macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF). TLR activate the necrosis factor kappa B (NF-kB) pathway leading to udregulation of adhesion molecules (Selectin P and E: adhesion of leukocytes; adhesion molecule-1 [ICAM-1] and vascular adhesion molecule-1 [VCAM-1]: macrophage proliferation) and cytokines (IL-6: express VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, inducting MCP-1 and up taking low-density lipoproteins [LDL]).